Computer Architecture
Category : Banking
Computer Architecture
Computer architecture deals with the functional behaviour of a computer system as viewed by a programmer. It can also be described as the logical structure of the system unit that housed electronic components. The computer architecture forms the backbone for building successful computer systems.

Components of Computer
A computer consists of following main components
Input Unit
The computer accepts coded information through input unit by the user. It is a device that is used to give required information to the computer, e.g. keyboard, mouse, etc.
An input unit performs the following functions
(i) It accepts the instructions and data from the user.
(ii) It converts these instructions and data in computer in acceptable format.
(iii) It supplies the converted instructions and data to the computer system for further processing.
Output Unit
This unit sends the processed results to the user. It is mainly used to display the desired result to the user as per input instruction, e.g. video monitor, printer and plotter, etc.
The following functions are performed by an output unit
(i) It accepts the results produced by the computer which are in coded form and hence cannot be easily understood by us.
(ii) It converts these coded results to human acceptable form.
(iii) It supplies the converted results to the user.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
It consists of set of registers, arithmetic logic unit and control unit, which together interpret and execute instructions in assembly language.
The primary functions of the CPU are as follow
(i) The CPU transfers instructions and input data from main memory to registers, i.e. internal memory.
(ii) The CPU executes the instructions in the stored sequence.
(iii) When necessary, CPU transfers output data from registers to main memory.
Central Processing Unit is often called the brain of computer. The CPU is fabricated as a single Integrated Circuit (1C) and is also known as microprocessor.
A CPU controls all the internal and external devices and performs arithmetic and logic operations.
The CPU consists of following main sub-systems
Arithmetic Logic Unit
ALU contains the electronic circuitry that executes all arithmetic and logical operations on the available data.
ALU uses registers to hold the data that is being processed.
Most ALUs can perform the following operations
(a) Logical operations (AND, NOT, OR, XOR)
(b) Arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication and division).
(c) Bit-shifting operations (shifting or rotating a word by a specified number of bit to the left or right with or without sign extension).
(d) Comparison operations (=, <, < =, >, > =)
|
Registers These are special purpose and high speed temporary memory units. Registers are not referenced by their address, but are directly accessed and manipulated by the CPU during execution. Registers store data, instructions, address and intermediate results of processing. The number and size of registers vary from processor to processor. |
Control Unit
CU coordinates with the input and output devices of a computer. It directs the computer to carry out stored program instructions by communicating with the ALU and the registers. It organises the processing of data and instructions. The basic function of control unit is to fetch the instruction stored in the main memory, identify the operations and the devices involved in it and accordingly generate control signals.
|
Microprocessor The microprocessor is the controlling element in a computer system and is sometimes referred to as the chip. Microprocessor is the main hardware that drives the computer. It is a large Printed Circuit Board (PCB), which is used in all electronic systems such as computer, calculator, digital system, etc. The speed of CPU depends upon the type of microprocessor used. · Intel 4004 was the first microprocessor made by Intel in 1971 by scientist Ted H off and engineer Frederico Fag gin. · Some of the popular microprocessors are Intel core i7, Intel, Dual core, Pentium /V, etc. |
Memory Unit
This unit is responsible to store programs or data on a temporary or permanent basis. It has primary memory (main memory) and secondary memory (auxiliary memory). The input data which is to be processed is brought into main memory before processing. The needed instruction for processing and any kind of intermediate results are also stored in primary memory. Together with these, the final output is also stored in primary memory before transferring it to the output unit. Another kind of memory is referred as secondary memory of a computer system. This unit is used to permanently store data, programs and output. This unit does not deal directly with CPU.
Motherboard
The main circuit board contained in any computer is called a motherboard. It is also known as the main board or logic board or system board or planar board. The biggest piece of silicon housed in the system unit of a computer is motherboard. All the other electronic devices and circuits of computer system are attached to this board like, CPU, ROM, RAM, expansion slots, PCI slots and USB ports. It also includes controllers for devices like the hard drive, DVD drive, keyboard and mouse. In other words, motherboard makes everything in a computer work together.
Interconnection of Units
CPU sends data, instructions and information to the components inside the computer as well as to the peripheral devices attached to it.
In other wouds, a bus is a set of wires used for interconnection, where each wire can carry one bit of data. In other words, bus is a set of electronic signal pathways that allows information and signals to travel between components inside or outside of a computer.
A computer bus can be divided into two types
Internal bus includes following buses
(i) The command to access the memory or the I/O device is carried by the control bus.
(ii) The address of I/O device or memory is carried by the address bus. The data to be transferred is carried by the data bus.
Tit- Bits
Instruction Cycle
The instruction cycle represents the sequence of events that takes place as an instruction is read from memory and executed.
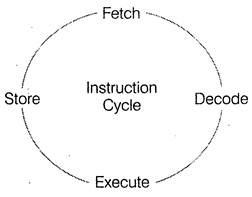
A simple instruction cycle consists of-the following steps
In above steps, step 1 and 2 instructions are same and known as fetch cycle and step 3 and 4 instructions are different and known as execute cycle.
Instructions Format
Computer understands instructions only in terms of 0's and 1's, which is called the machine language. A computer program is a set of instructions that describe the steps to be performed for carrying out a computational task. The processor must have two inputs; instructions and data.
The instructions tell the processor what actions are needed to be performed on the data. An instruction is further divided into two parts; operation (op-code) and operand. The op-code represents action that the processor must execute and the operand defines the parameters of the action and depends on the operation.
Tit- Bits
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
