Introduction to Computer
Category : Banking
Introduction to Computer
A computer is an electronic machine that accepts data from the user, processes the data by performing calculations and operations on it and generates the desired output as a result. The term computer is derived from the Latin word 'computare' which means 'to compute'.
Generally, computer is the combination of Hardware and Software which converts data into information. Computer operates on set of instructions only, they cannot think as human being. Computer has an ability to store and execute set of instructions called program which makes it extremely distinguishable and versatile than calculators. Computer makes people's lives easier and more comfortable.

Functioning of a Computer
Computer Performs four basic functions -which are as follows
Features of Computer
The key features of computer are as follows
Terms Related to Computer
History of Computer
Computer is not the creation of one day, rather it took a long period for the development of modern computer. History of computer is described in this table
|
Invention |
Inventor |
Characteristics |
Applications |
|
Abacus 1602 |
China |
· First mechanical, calculating device. · A horizontal rod represents the one, tens, hundred, etc. |
· Used for addition and subtraction operations. Calculation of square roots can also be performed. |
|
Napier's Bones 1617 |
John Napier |
· Three dimensional structure. · Holding numbers from 0 to 9 only. · Represent graphical structure of calculating result. |
· Perform multiplication on numbers. · Technology used for calculation called Rabdologia. |
|
Pascaline , 1642 |
Blaise Pascal |
· First mechanical adding machine. · It was structured like rectangular box, with eight disc (represent number of units). |
· Perform addition and subtraction of two numbers. Mainly designed with regard to the pressure of liquid. |
|
Jacquard's Loom 1801 |
Joseph Marie Jacquard |
· Mainly weaved a silk based pattern. Used punched card for the sequence of operation. |
· Simplified the process of Textiles. |
|
Analytical Engine 1837 |
Charles Babbage (Father of computer) |
· First general-purpose computer. · Stored program in the form of 'pegs' also called barrels. |
· It was a decimal machine used sign and magnitude for representation of a number. |
|
Tabulating Machine 1880 |
Herman Hollerith |
· It used punched cards with round holes. It was the first electromechanical machine, designed to process the data for census in 1890. |
· Read one card at a time. |
|
MARK-1 1944 |
Howard Aiken |
· Consists of interlocking panels of small glass, counters, switches and control circuits. · Data can be entered manually. |
· Mainly used in the war effort during World War-II · Magnetic drums are used for storage. |
|
ENIAC 1946 |
JP Eckert and JW Mauchly |
· It is a combination of twenty accumulators. · First electronic digital computer. |
· Used for weather prediction, atomic energy calculation and other scientific uses. |
|
EDSAC 1949 |
John Von Morris Wilcus |
· It was first computer which provided storage capacity. · First computer program was run on machine. |
· Capable of storing instructions and data in memory. · Used mercury delay lines for memory, vacuum tubes for logic. |
|
UNIVAC 1951 |
Eckert John Mauchly |
· First general-purpose electronic computer with large amount of input and output. |
· Used magnetic tapes as input and output. |
|
IBM-650 Computer 1954 |
IBM Company |
· Provided input/output units converting alphabetical and special characters to two-digit decimal code. |
· Payroll processing · Oil refinery design · Market research analysis |
Generations of computer
A generation refers to the state of improvement in the development of system. Computers are built of electromechanically, before generation. Each generation of computer is characterised by a major echnological development that fundamentally changed the way, computers operate.
|
Generation |
Switching Device |
Storage Device |
Speed |
Operating system |
Language |
Characteristics |
Applications |
|
First (1940-56) |
Vacuum tubes |
Magnetic drums |
333 micro second
|
Batch operating system |
Machine language(Binary number 0's and 1's) |
Fastest computing device Generate large amount of heat. Non-portable. |
Used for scientific purpose e.g. ENIAC, UNIVAC, MARK-1, etc. |
|
Second(1956-63) |
Transistors (Made up of semiconductor)
|
Magnetic core technology |
10 micro seconds |
Time sharing system, Multitasking OS |
Assembly language, high level language |
More reliable and less prone to hardware failure. Portable and generate less amount of heat. |
Used for commercial production e.g. PDP-8, IBM-1401, etc. |
|
Third (1964-71) |
Integrated Circuits(ICs) (Made up of silicon) |
Magnetic core as primary storage medium |
100 Nano seconds |
Real-time system |
High level language(FORTRAN, COBOL, ALGOL) |
Consumed less power. Highly sophisticated technology required. |
Database management system e.g. NCR-395. B6500,etc. |
|
Fourth (1971- Present) |
Large Scale Integrated (LSI) circuit microprocessor |
Semi-conductor memory Winchester disk |
300 Nano seconds |
Time sharing, GUI interface. |
PASCAL, ADA, COBOL-74 FORTRAN IV |
More reliable and portable. This generation leads to better communication and resource sharing |
Distributed system, e.g. Intel 4004 chip, Macintosh. |
|
Fifth(Present and Beyond) |
Super Large Scale Integrated (SLSI) chips |
Optical disk - |
- |
Knowledge Information Processing system |
- |
Parallel processing. Intel core microprocessor is implemented. Enables mega chips. |
Artificial intelligence e.g. Robotics |
Classification of Computer
Computers are mainly classified as three types as follows
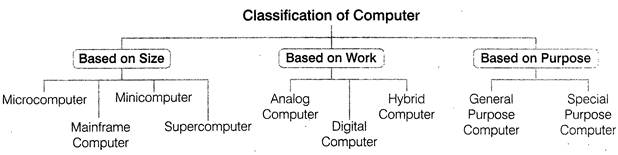
Based on Size
On the basis of size, computers are categorised as follows
Microcomputer
Microcomputers are the least powerful, yet the most widely used and fastest growing type of computers and are also called portable computers. Microcomputer consists of three basic categories of physical equipment, i.e. system unit, input/output unit and memory unit.
Some types of microcomputer are as follows
(a) Desktop Computer or Personal Computer (PCs) These are small, relatively inexpensive computers. These are based on the microprocessor technology (Integrated Circuit, 1C). In 1958, Jack Kilby and Robert Noyce invented the first 1C.
(b) Laptop These computers are also known as ultra-book or notebook. These are portable, lightweight and fit into most briefcases. They include rechargeable battery, so these can work anywhere.
(c) Handheld Computer These are the smallest and are designed to fit into the palm. So, these are also known as Palmtop. They are practical for certain functions such as phone books and calendars. They use the pen for input instead of keyboard.
(d) Tablet Computer They have key features of the notebook computer, but these can accept input from a pen instead of the keyboard or mouse.
(e) Personal Digital Assistant (PDA) It is also known as a handheld PC, or personal data assistant, is a mobile device that functions as a personal information manager.
Minicomputer
Minicomputers are smaller in size, faster, costlower than mainframe computers. Initially, the minicomputer was designed to carry out some specific tasks, like engineering and Computer Aided Design (CAD) calculations. But now, they are being used as central computer which is known as Server. Minicomputers are IBM-17, DEC PDP-11, HP-9000, etc.
Mainframe Computer
Mainframe computers are those having large internal memory storage and comprehensive range of software. Mainframe computer serves as a backbone for the entire business world. It is considered as the heart of a network of computers or terminals that allows a large number of people to work at the same time. Mainframe computers are IBM-370, IBM-S/390, UNIVAC-1110, etc.
Supercomputer
Supercomputers are the fastest and most expensive machines. They have high processing speed compared to other computers. The speed of supercomputers are measured in FLOPS (Floating Point Operations Per Second). Supercomputers are used for highly calculation intensive tasks, such as weather forecasting, nuclear research, military agencies and scientific research laboratories. Supercomputers are most powerful, large in size and memory, compared to all other computers.
Based on Work
On the basis of' work, computers are categorised as follow
Analog Computer
Analog computers are the job-oriented computers. They carry out arithmetic and logical operations by manipulating and processing of data. e.g. speedometers, seismograph, etc. Analog computer can perform several mathematical operations simultaneously. It uses continuous variables for mathematical operations and utilizes mechanical or electrical energy.
Digital Computer
Digital computers work by calculating the binary digits. A digital computer, not only performs mathematical calculations, but also combines the bytes to produce desired graphics, sounds. e.g. desktop (PC),
Hybrid Computer
Hybrid computers are the combination of analog and digital computers. Machines used in hospitals like ECG and DIALYSIS are the commonly used hybrid computers.
Based on Purpose
On the basis of purpose, computers are categorised as follow
General Purpose Computer
General purpose computers are those computers, which are used to solve variety of problems by changing the program or instructions, e.g. to make small database, calculations, accounting, etc.
Special Purpose Computer
Special purpose computers are those computers which are used to solve a single and dedicated type of problem, e.g. automatic aircraft landing, multimedia computer, etc.
|
Quantum computer was first introduced by Richard Feynman. It uses quantum mechanical phenomena It is the fastest computer imitating brain working. |
Applications of Computer
Now-a-days computers have been employed in almost all the aspects of professional and personal life. Some of the areas Where computers are being used are as follows
temperature, pressure, volume are monitored and controlled by computers. Robotics developed with the help of computers, plays a very crucial role here.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
