Computer Hardware
Computer hardware is the collection of physical parts of a computer system. This includes the computer case, monitor, keyboard, and mouse. It also includes all the parts inside the computer case, such as the hard disk drive, motherboard, video card, and many others. Computer hardware is what you can physically touch.
All computers have a common structure. These components can be very different in terms of expense, speed and quality, but every computer has them to one degree or another.
The main components are as follows:
- Form Factor: This is the physical configuration of the computer: desktop, laptop, tablet or netbook
- The Processor: This is the 'brain' of the computer
- Data Storage: This is where your data are stored, as well as all the programmers and other files that your computer needs to run.
- The Operating System: The OS is the software that runs the computer on the lowest level - Windows,
- Macintosh or Linux are the most popular.
- Monitor: This is the viewing screen that you use to operate the computer. It is a very important part of the digital photography computer.
HARDWARE COMONENTS OF COMPUTER
- The Processor: The Processor (CPU) is the "brain" of your computer, the thing that carries out the tasks you give it. The speed that the computer can run an operation is largely determined by how fast the processor can make calculations. The CPU (Central Processing Unit), a complete computation engine that is fabricated on a single chip, is the computer's brain. It is sometimes referred to as the central processor, microprocessor, or just processor.
Two typical components of a CPU are:
(1) The Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), which performs arithmetic and logical operations.
(2) The Control Unit, which extracts instructions from memory and decodes and executes them, calling on the ALU when necessary.
There are three parts to determining how feat a processorcan do its work: clock speed, number of cores, and chip generation.
- Clock Speed: Every processor has a speed rating, currently measured in Gigahertz or GHz. The higher the number, the faster it runs. In theory, a processor that is 2GHz will be twice as fast as a 1 GHz.
- Number of Cores: A core refers to part of the processor that actually does the calculations. One way that computer chip makers have increased the speed is by adding additional cores. A dual core processor can run operations twice as fast as a single core processor of the same design and clock speed. Multiple cores can make some computing tasks go quickly, and for others, there is no speed increase at all. In many cases, both clock speed and number of cores is less important than the chip generation.
- Chip Generation: Every few years, the companies that make processor chips will redesign the entire chip architecture to make them faster. Sometimes the clock speed of the newer chips will be slower, even as the real-world speed of the chip increases.
- Intel's Core 2 Duo chips that run at 3 GHz, for instance, will run Photoshop slower than an i7 chip running at 2 GHz, because the i7 is a newer generation.
There are 2 main chip manufacturers, Intel and AMD.
As of 2013, the current lineup of core processors includes the latest Intel core i7, Intel core i5, and Intel core i3, and the older Intel core 2 solo, Intel core 2 Duo, Intel core 2 Quad, and Intel core 2 Extereme lines.
- The Motherboard: The motherboard connects all the other components to one another, and is the physical base upon which everything build. It contains a lot of machine's core features, like the number of USB ports, the number of expansion cards can put in (such as video, sound, and Wi-Fi), and also partially determines how big a computer will be. Which motherboard can be pick will depend on whether want to build a low, medium, or high performance machine and how advanced of a user you are.
- The Case: The case holds all of your computer's parts together. For the most part, a case is less about features that affect how computer runs and more about features that affect you and your home—that is, how quiet it is, how large it is, and of course, how it looks in office/home.
- The RAM: RAM, or Random Access Memory (or "Memory" for short), is like your computer's short- term memory. It stores data what a computer needs quick access to to help your programs run faster, and help to run more programs at one time.
- The Graphics Card: The Graphics card, or GPU, is a processor specifically designed to handle graphics. It's what you hook your monitor up to, and it's what draws your desktop and your windows on the screen. Some motherboards come with a GPU already integrated, which is enough to manage your desktop, but not enough for watching high definition video or playing 3D games. For those, you'll need a dedicated graphics card, since it can do the legwork needed to draw those complex images.
- The Hard Drive(s): Hard drive store all of data, ranging from operating system to documents, music, and movies. If the RAM is considered as computer's short-term memory, then hard drive is the long-term memory. It stores all the things want to keep around for a while. The kind of hard drive choose will be determined mainly by how much data need to store.
- The Optical Drive: An optical drive, more commonly known as a CD or DVD drive, is what required to read CDs, DVDs, and even Blu-Ray discs.
- The Power Supply: The power supply directs electricity to the other components in machine. Generally, if you have a high performance computer with a fast processor, a graphics card, and a few hard drives, you'll need a higher wattage power supply than you would if you were building a low-end PC.
- Sound Card: A sound card is an electronic circuit board that is mounted inside the computer to control sound output to speakers or headphones, to record sound input from a microphone connected to the computer, and to manipulate sound stored on a disk. Sound cards are essential for multimedia applications and have become common on modem personal computers.
- Ports: A port is an interface on a computer to which you can connect a device. Personal computers have various types of ports. Internally, there are several ports for connecting disk drives, monitors, and keyboards. Externally, personal computers have ports for connecting modems, printers, mice, and other peripheral devices.
There are three common types of external ports that usually come with a computer:
(i) Parallel ports (for most printers): A parallel part is an interface for connecting eight or more data wires. The data flows through the eight wires simultaneously. They can transmit eight bits of data in parallel. As a result, parallel ports provide high speed data transmission. Parallel port is used to connect printer to computer.
(ii) Serial ports (for most modems and some mouse): A serial port transmits one bit of data through a single wire. Since, data is transmitted serially as single bits. Serial ports provide slow speed data transmission. Serial port is used to connect external modems, plotters, barcode, reader etc.
(iii) USB (Universal Serial Bus) ports (for about every peripheral made in a USB version): The USE (Universal Serial Bus) provides a single, standardized, easy-to-use way to connect up to 127 devices to a computer. The USB connectors let you attach everything from mice to printers to your computer more quickly and easily than the other two. The operating system supports USB as well, so the installation of the device drives is quick and easy, too.
A “bus” is a set of conductors that carry signals between different parts of a computer
Fire wire: It is used to connect audio and video multimedia devices like video camera it has data transfer rateofupto400Mb/s.
- Input Output Peripherals: A computer peripheral is any external device that provides input and output for the computer. For example, a keyboard and mouse are input peripherals, while a monitor and printer are output peripherals. Computer peripherals, or peripheral devices, are sometimes called "I/O devices" because they provide input and output for the computer. Some peripherals, such as external hard drives, provide both input and output for the computer.
- Expansion card: An expansion card is an electronic card/board that is used to add extra functionality to a computer. It is inserted into an expansion slot on the motherboard of a computer. Expansion cards contain edge connectors that are used to create an electronic link between motherboard and card, thus enabling these two to communicate.
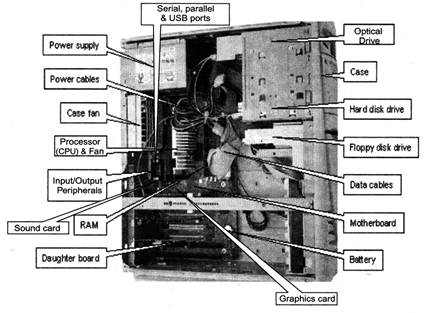
Hardware Component of Computer

