Dihydric Alcohols
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
These are compound containing two hydroxyl groups. These are dihydroxy derivatives of alkanes. Their general formula is \[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n+2}}{{O}_{2}}\]. The simplest and most important dihydric alcohol is ethylene glycol. They are classified as \[\alpha ,\,\,\beta ,\,\,\gamma .....\]glycols, according to the relative position of two hydroxyl groups. \[\alpha \] is 1, 2 glycol, \[\beta \] is 1, 3 glycol.
(1) Preparation
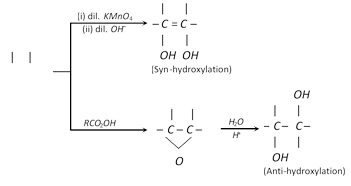
(i) From ethylene : (a) Through cold dilute alkaline solution of Bayer’s reagent
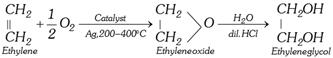
(b) With \[{{O}_{2}}\] in presence of Ag :
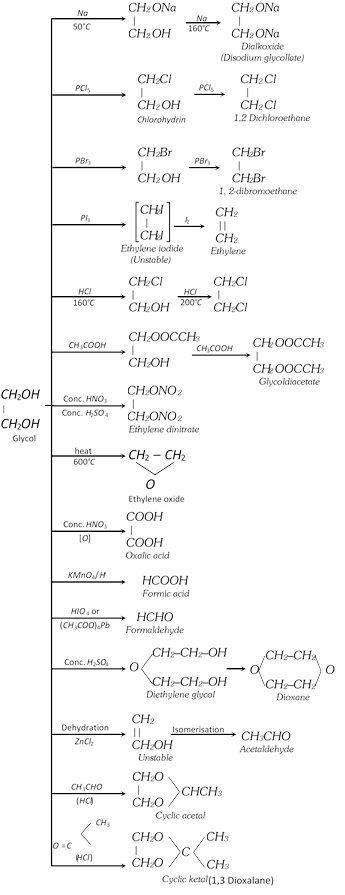
(c) With HOCl followed by hydrolysis : (Industrial method)
\[\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}}}\, \\C{{H}_{2}} \\\end{matrix}+HOCl\to \underset{\text{Ethylenechlorohydrin}}{\mathop{\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}OH}}\, \\C{{H}_{2}}Cl\,\,\, \\\end{matrix}}}\,\]\[\xrightarrow{NaHC{{O}_{3}}}\underset{\text{Glycol}}{\mathop{\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}OH}}\, \\C{{H}_{2}}OH \\\end{matrix}}}\,+NaCl+C{{O}_{2}}\]
(ii) From 1, 2 dibromo ethane [Lab method]:
\[\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}Br}}\,\\C{{H}_{2}}Br\\\end{matrix}+N{{a}_{2}}C{{O}_{3}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}OH}}\,\\C{{H}_{2}}OH\\\end{matrix}+2NaBr+C{{O}_{2}}\]
\[\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}Br}}\,\\C{{H}_{2}}Br\\\end{matrix}+2C{{H}_{3}}COOK\underset{-2KBr}{\mathop{\xrightarrow{C{{H}_{3}}COOH}}}\,\underset{\text{Glycoldiacetate}}{\mathop{\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}OOCC{{H}_{3}}}}\,\\C{{H}_{2}}OOCC{{H}_{3}}\\\end{matrix}}}\,\xrightarrow{NaOH}\begin{matrix}\underset{|\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,}{\mathop{C{{H}_{2}}OH}}\,\\C{{H}_{2}}OH\\\end{matrix}+2C{{H}_{3}}COONa\]
(2) Physical properties
(i) It is a colourless, syrupy liquid and sweet in taste. Its boiling point is \[{{197}^{o}}C\].
(ii) It is miscible in water and ethanol in all proportions but is insoluble in ether.
(iii) It is toxic as methanol when taken orally.
(iv) It is widely used as a solvent and as an antifreeze agent.
(3) Chemical properties
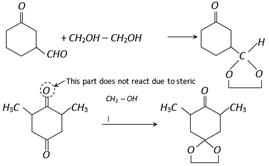
Dioxalane formation provides a path of protecting a carbonyl group in reaction studied in basic medium in which acetals are not affected. The carbonyl compound may be regenerated by the addition of periodic acid to aqueous solution of the dioxalane or by acidic hydrolysis.
![]()
\[\xrightarrow{HI{{O}_{4}}}R-CO-R+2HCHO\]
Aldehyde is more reactive than ketone in dioxalane formation.
(4) Uses
(i) Used as an antifreeze in car radiators.
(ii) Used in the manufacture of dacron, dioxane etc.
(iii) As a solvent and as a preservatives.
(iv) As a cooling agent in aeroplanes.
(v) As an explosives in the form of dinitrate.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
