Current Density (J )
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
Current density at any point inside a conductor is defined as a vector having magnitude equal to current per unit area surrounding that point. Remember area is normal to the direction of charge flow (or current passes) through that point.
(1) Current density at point P is given by \[\overrightarrow{J\,}=\frac{di}{dA}\overrightarrow{n\,}\]
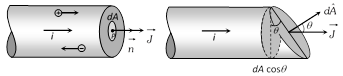
(2) If the cross-sectional area is not normal to the current, but makes an angle \[\theta \] with the direction of current then
\[J=\frac{di}{dA\cos \theta }\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[di=JdA\cos \theta \] \[=\overrightarrow{J\,}.\overrightarrow{dA}\]\[\Rightarrow \] \[i=\int{\overrightarrow{J\,}\cdot \,\overrightarrow{dA}}\]
(3) If current density \[\overrightarrow{J\,}\] is uniform for a normal cross-section \[\overrightarrow{A\,}\] then \[J=\frac{i}{A}\]
(4) Current density \[\overrightarrow{J\,}\] is a vector quantity. It's direction is same as that of \[\overrightarrow{E}\] . It's S.I. unit is \[amp/{{m}^{2}}\] and dimension \[[{{L}^{-2}}A]\].
(5) In case of uniform flow of charge through a cross-section normal to it as \[i=nqvA\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[J=\frac{i}{A}=nqv\].
(6) Current density relates with electric field as \[\overrightarrow{J}=\sigma \,\overrightarrow{E}=\frac{\overrightarrow{E}}{\rho }\]; where \[\sigma =\] conductivity and \[\rho =\] resistivity or specific resistance of substance.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
