Self Induction
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
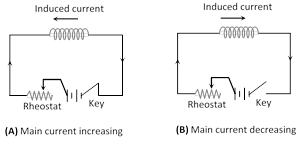
Whenever the electric current passing through a coil or circuit changes, the magnetic flux linked with it will also change. As a result of this, in accordance with Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction, an emf is induced in the coil or the circuit which opposes the change that causes it. This phenomenon is called 'self induction' and the emf induced is called back emf, current so produced in the coil is called induced current.
(1) Coefficient of self-induction : Number of flux linkages with the coil is proportional to the current i. i.e. \[N\varphi \propto i\] or \[N\varphi =Li\] (N is the number of turns in coil and \[N\phi -\]total flux linkage). Hence \[L=\frac{N\varphi }{i}\]= coefficient of self-induction.
(2) If \[i=1\,amp,\,\,N=1\] then, \[L=\phi \] i.e. the coefficient of self induction of a coil is equal to the flux linked with the coil when the current in it is 1 amp.
(3) By Faraday's second law induced emf \[e=-N\frac{d\varphi }{dt}\]. Which gives \[e=-L\frac{di}{dt}\] ; If \[\frac{di}{dt}=1\,amp/sec\]then \[|e|\,=L\]
Hence coefficient of self induction is equal to the emf induced in the coil when the rate of change of current in the coil is unity.
(4) Units and dimensional formula of 'L' : It's S.I. unit
\[\frac{weber}{Amp}=\frac{Tesla\times {{m}^{2}}}{Amp}=\frac{N\times m}{Am{{p}^{2}}}=\frac{Joule}{Am{{p}^{2}}}=\frac{Coulomb\times volt}{Am{{p}^{2}}}\]
\[=\frac{volt\times \sec }{amp}=ohm\times \sec \]. But practical unit is henry (H). It's dimensional formula \[[L]=[M{{L}^{2}}{{T}^{-2}}{{A}^{-2}}]\]
(5) Dependence of self inductance (L) : 'L' does not depend upon current flowing or change in current flowing but it depends upon number of turns (N), Area of cross section (A) and permeability of medium \[(\mu )\].
'L' does not play any role till there is a constant current flowing in the circuit. 'L' comes in to the picture only when there is a change in current.
(6) Magnetic potential energy of inductor : In building a steady current in the circuit, the source emf has to do work against of self inductance of coil and whatever energy consumed for this work stored in magnetic field of coil this energy called as magnetic potential energy (U) of coil
\[U=\int_{\,0}^{\,i}{\,Lidi}=\frac{1}{2}L{{i}^{2}}\]; Also \[U=\frac{1}{2}(Li)i=\frac{N\varphi i}{2}\]
(7) The various formulae for L
| Condition | Figure |
| Circular coil \[L=\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}\pi {{N}^{2}}r}{2}\] | 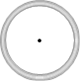 |
| Solenoid \[L=\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{\mu }_{r}}{{N}^{2}}A}{l}=\frac{\mu {{N}^{2}}A}{l}(\mu ={{\mu }_{0}}{{\mu }_{r}})\] | 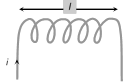 |
| Toroid \[L=\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}{{N}^{2}}r}{2}\] | 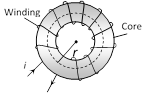 |
| Square coil \[L=\frac{2\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}{{N}^{2}}a}{\pi }\] | 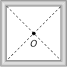 |
| Coaxial cylinders \[L=\frac{{{\mu }_{0}}}{2\pi r}{{\log }_{e}}\frac{{{r}_{2}}}{{{r}_{1}}}\] \[\frac{2.303}{2\pi r}{{\mu }_{0}}{{\log }_{10}}\frac{{{r}_{2}}}{{{r}_{1}}}\] | 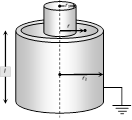 |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
