Moving Coil Galvanometer
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
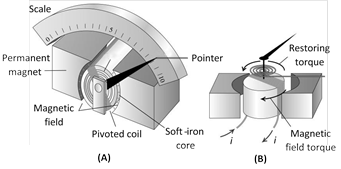
In a moving coil galvanometer the coil is suspended between the pole pieces of a strong horse-shoe magnet. The pole pieces are made cylindrical and a soft iron cylindrical core is placed within the coil without touching it. This makes the field radial. In such a field the plane of the coil always remains parallel to the field. Therefore \[\theta ={{90}^{o}}\] and the deflecting torque always has the maximum value.
\[{{\tau }_{\text{def}}}=NBiA\] ......(i)
Coil deflects, a restoring torque is set up in the suspension fibre. If \[\alpha \] is the angle of twist, the restoring torque is
\[{{\tau }_{\text{rest}}}=C\alpha \] .....(ii)
where C is the torsional constant of the fibre.
When the coil is in equilibrium \[NBiA=C\alpha \Rightarrow i=Ka,\]
where \[K=\frac{C}{NBA}\] is the galvanometer constant. This linear relationship between i and a makes the moving coil galvanometer useful for current measurement and detection.
Current sensitivity \[\mathbf{(}{{\mathbf{S}}_{\mathbf{i}}}\mathbf{)}\] : The current sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as the deflection produced in the galvanometer per unit current flowing through it.
\[{{S}_{i}}=\frac{\alpha }{i}=\frac{NBA}{C}\]
Voltage sensitivity \[\mathbf{(}{{\mathbf{S}}_{\mathbf{V}}}\mathbf{)}\] : Voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer is defined as the deflection produced in the galvanometer per unit voltage applied to it.
\[{{S}_{V}}=\frac{\alpha }{V}=\frac{\alpha }{iR}=\frac{{{S}_{i}}}{R}=\frac{NBA}{RC}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
