General Characteristics Of Arenes
Category : JEE Main & Advanced
(1) All arenes have general formula \[[{{C}_{n}}{{H}_{2n}}-6y]\]. Where y is number of benzene rings and n is not less than 6.
(2) Arenes are cyclic and planar. They undergo substitution rather than addition reactions.
(3) Aromaticity or aromatic character : The characteristic behaviour of aromatic compounds is called aromaticity. Aromaticity is due to extensive delocalisation of p-electrons in planar ring system. Huckel (1931) explained aromaticity on the basis of following rule.
Huckel rule : For aromaticity the molecule must be planar, cyclic system having delocalised \[(4n+2)\pi \]electrons where n is an integer equal to 0, 1, 2, 3, ………….
Thus, the aromatic compounds have delocalised electron cloud of 2,6,10 or 14 \[\pi \] electrons.

Similarly cyclolpentadienyl anion or tropylium ion are also aromatic because of containing \[6\pi \] electrons \[(n=1)\].
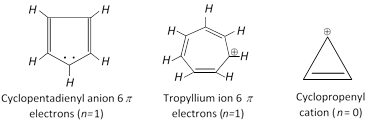
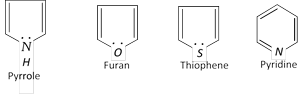
Hetrocyclic compounds also have 6p electrons (n = 1).
Molecules do not satisfy huckel rule are not aromatic.


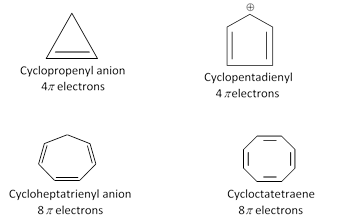
(4) Antiaromaticity : Planar cyclic conjugated species, less stable than the corresponding acyclic unsaturated species are called antiaromatic. Molecular orbital calculations have shown that such compounds have \[4n\pi \] electrons. In fact such cyclic compounds which have \[4n\pi \] electrons are called antiaromatic compounds and this characteristic is called antiaromaticity.
Example : 1,3-Cyclobutadiene, It is extremely unstable antiaromatic compound because it has \[4n\pi \] electrons \[(n=1)\] and it is less stable than 1,3 butadiene by about 83.6 \[83.6\,\,KJ\,\,mo{{l}^{-1}}\].
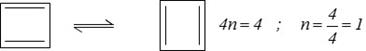
Thus, cyclobutanediene shows two equivalent contributing structures and it has \[n=1\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
