Extra Embryonic Membrane
Category : NEET
Extra embryonic membrane
An aquatic embryo is surrounded by water, which protects the embryo, keep it moist, removes wastes and permits gas exchange. In land vertebrate (reptiles, birds and mammals), these functions are taken over by the extra embryonic membranes. These membranes are formed outside the embryo from the trophoblastic only in amniotes and perform specific function. Some of these membranes take part in the formation of placenta in mammals.
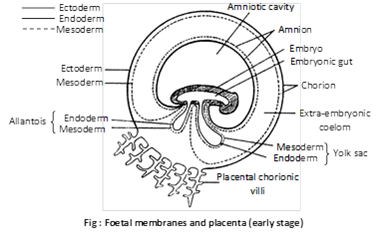
(i) Yolk sac: It is formed below the embryo. It contains fluid, not yolk. The yolk sac is a vestigial organ inherited from the oviparous reptilian ancestors. Yolk sac encloses by outer mesoderm and inner endodermal layer.
Function: It is mainly digestive in function. It also absorbs the dissolved yolk and passes it to developing embryo in reptiles, birds and prototherian. In human beings, it is vestigial. In human embryo it act as the site of blood cell formation until about the 6th week, when the liver takes over this role.
(ii) Amnion: It is formed above the embryo. It consist of outer mesoderm and inner ectoderm. The amnion and the fluid filled amniotic cavity it encloses, enlarge and nearly surround the embryo. The embryo is suspended in the amniotic cavity by an umbilical cord. The latter is formed of the stalks of the yolk sac and allantois. The main blood vessel from the placenta reach the foetus through the umbilical cord. Amniotic fluid secreted by both embryo and amnion. The cells of amniotic fluid are the basis of parental test called amniocentesis, for the sex of the foetus and for checking chromosomal defects in it.
(1) The amniotic fluid cushions the embryo.
(2) It protecting embryo against bumps and bacterial infections.
(3) It maintains a constant temperature and pressure.
(4) It protects the embryo from jerk, injury and shocks.
(5) It prevents desiccation of the embryo.
(iii) Allantois: It is a fold of splanchnopleur developed from the hind gut of the embryo. It consist of outer mesoderm and inner endoderm. It is well developed in amniotes with polylecithal egg (e.g. reptiles, birds and prototherians) and stores the nitrogenous waste of the embryo so act as extra embryonic kidney. In most of eutherians, it combines with chorion to form allantochorion placenta. But in man it remains small or reduced and does not reach the chorion. However, it forms umbilical arteries and veins which grow up to the chorion to vascularise it.
(1) The cavity of the allantois serves as a urinary bladder. It stores the protein breakdown product in the form of water-insoluble crystals of uric acid and inside the egg up to the time of hatching. But with the acquisition of viviparity in the marsupials and the placental mammals, the original function of the allantois as a urinary bladder becomes altogether lost.
(2) The vascular “chorioallantoic membrane” lies in a close proximity to the inner surface of the porous shell. It acts as an extra embryonic lung by supplying the embryo with oxygen.
(3) Together with the chorion, the allantois also surrounds the albumen to form the albumen sac and thus assists in the absorption of nutritionally rich albumen.
(4) In mammals, allantois supply oxygen and nutrient to the embryo.
(iv) Chorionic: It is outermost fold of somatopleur (outer ectoderm and somatic mesoderm) and surrounds the embryo. In reptile’s birds and prototherians, allantochorion act as extra embryonic lungs help in exchange of gases. But in primates including human beings, only chorion forms the placenta (chorionic placenta).
Function: It protects the embryo and forms placenta for metabolic exchange between the foetus and the mother.
Types and functions of extra embryonic membrane
|
S. No. |
Name of membrane |
Characteristics and functions |
Remarks |
|
(1) |
Yolk sac |
(1) Formed by inner endoderm and outer mesoderm (= splanchnopleura) (2) Digestive function (= extra embryonic duct) (3) Absorbs dissolved yolk and supplicate it to developing embryo. |
Vestigeal in humans.
Well developed in reptiles, bird and prototherians. |
|
(2) |
Amnion |
(1) Formed by inner ectoderm and outer mesoderm (somatopleur) above the embryo. (2) Between the embryo and amnion there is a cavity called amniotic cavity filled with amniotic fluid secreted by amnion and embryo. (3) Amniotic fluid act as shock absorber and prevent desiccation of embryo. (4) Ex-foliated embryonic (= foetal) cells are used for (a) pre-natal sex determination (b) congenital defects (c) inborn metabolic disorders. This technique is called amniocentesis. |
Well developed in all amniotes |
|
(3) |
Allantois |
Develops as fold of splanchnopleur; developed from gut of embryo. |
(1) In placentals, it combines with chorion to form allanto-chorion placenta. (reduced in human) (2) Acts as extra-embryonic kidney in reptiles, birds and prototherians. |
|
(4) |
Chorion |
Outermost fold of somatopleur and surrounds the embryo |
(1) Takes part in forming the true chorio allantoic placenta (2) Acts as extra-embryonic lung in reptiles, birds and prototherians. |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
