Human Physiology
Category : SSC
Introduction
\[\frac{Upper\,\,jaw}{Lower\,\,jaw}=\frac{IC\,PmM}{IC\,PmM}=\frac{2123}{2123}\]
|
Name of the Digestive |
Name of the enzymes |
Substrate |
End product |
|
Saliva |
Ptyalin (Salivary amylase) |
Starch |
Maltose |
|
Pancreatic iuice |
Amylopsin (pancreatic amylase) |
Starch, Glycogen |
Maltose and Glucose |
|
Intestinal juice |
Sucrase (invertase), Maltase, Lactase |
Sucrose; Maltose, Lactose |
Glucose and fructose. Glucose, Glucose and galactose |
|
Gastric iuice |
Pepsin, Rennin |
Proteins, Casein |
Proteoses and peptones, Calcium casemate |
|
Pancreatic iuice |
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxyl peptidases |
Proteins, Proteins Peptides |
Proteoses and peptides Peptides Amino add. |
|
Intestinal juice |
Amino peptidase, Dipeptidase |
Peptides |
Amino acids, Amino acids |
|
Vitamin |
Chemical Name |
Function In Body |
Deficiency Disease |
|
\[{{B}_{1}}\] |
Thiamine pyrophosphate |
Part of coenzyme for respiration |
Beri-beri: nerve and heart disorders |
|
\[{{B}_{2}}\] |
Ribo flavin |
Part of coenzyme FAD needed for respiration |
Ariboflavinosis: skin and eye disorders |
|
\[{{B}_{12}}\] |
Cyanocobalamin |
Coenzyme needed for making red blood cells, bone, blood and nerve changes |
Pernicious anaemia |
|
\[{{B}_{5}}\] |
Nicotinic acid ('niacin') |
Part of coenzymes NAD, NADP used in respiration |
Pellagra: skin, gut and nerve disorders |
|
C |
Ascorbic acid |
Not precisely known |
Scurvy: degeneration of skin teeth and blood vessels. |
|
A |
Retinol |
Not fully known but forms part of visual pigment, rhodopsin |
Xeropthalmia: 'dry eyes' |
|
D |
Cholecalciferol |
Stimulates calcium absorption by small intestine, needed for proper bone growth |
Rickets: bone deformity |
|
E |
Tocopherol |
Not precisely known |
Infertility |
|
K |
Phylloquinone |
Involved in blood clotting |
Possible haemorrage |
|
Element |
Common ions |
Functions in human body |
|
Calcium |
\[C{{a}^{2+}}\] |
Calcium ions are needed for stability of cell membranes, as cofactors for some enzymes and are involved in muscle contraction and blood clotting. |
|
Phosphorus |
\[{{H}_{2}}P{{O}_{4}}\] |
Bones component of many organic molecules like DNA, RNA and ATP. |
|
Potassium Sodium Chlorine |
\[\left. \begin{align} & {{K}^{+}} \\ & N{{a}^{+}} \\ & C{{l}^{-}} \\ \end{align} \right\}\] |
These ions are important in determining the balance of electrical charges in body fluids. |
|
Iron |
\[F{{e}^{2+}},F{{e}^{3+}}\] |
Component of haemoglobin and cytochrome molecules. |
|
Iodine |
\[{{I}^{-}}\] |
Component of hormone thyroxin. |
|
Copper Manganes Zinc |
\[\left. \begin{align} & C{{u}^{2+}} \\ & M{{n}^{2+}} \\ & Z{{n}^{2+}} \\ \end{align} \right\}\] |
Trace elements as enzyme cofactors, for example, \[C{{u}^{2+}}\]is co-factor for cytochrome oxidase. |
Human Respiratory System
Blood Groups
Table: Blood Groups and Donor Compatibility
|
Blood Group |
Antigens on RBCs |
Antibodies in plasma |
Donor?s group |
|
A |
A |
anti-B |
A,O |
|
B |
B |
anti-A |
B,O |
|
AB |
A, B |
Nil |
AB, A, B, O |
|
O |
nil |
anti-A, B |
O |
Circulatory Pathways
A continuous or sustained rise in arterial pressure is known as hypertension. High blood pressure compels heart to work excessive and then can tend to congestive heart disease.
Excretion
Skeletal System
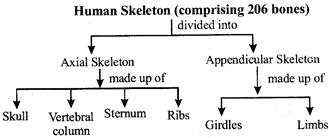
(i) Skull is made up of 29 bones. It is composed of
(ii) Vertebral column: 33 in babies, 26 in adults. Grouped into 5 categories: Cervical - 7; Thoracic -12; Lumber - 5; Sacral - 5; Coccygeal - 4 (fused in adults).
(iii) Sternum: Composed of 3 parts \[\to \] Manubrium, body of sternum and xiphoid process.
(iv) Ribs: They are twelve pairs. First seven pairs are true ribs. The 8th, 9th and 10th ribs are called false ribs or vertebrochondrial ribs. The last 11th and 12th pairs are called floating ribs.
(i) Girdles: 2 types - pectoral and pelvic.
(ii) Limb bones: Hind limbs and fore limbs - both made up of 30 bones each. .
Synovial Joints - Movable Joints: They are characterized by the presence of a closed space or cavity between the bones.
- Plane (gliding joint): Present between carpals. Only sliding motion in all direction is allowed.
- Hinge joint: Present between Knees joint
- Pivot joint: Present between atlas and axis
- Saddle joint: Present between carpal and metacarpal
- Ball and Socket joint: Present between humerus and pectoral girdle.
The human brain is divisible into three parts:
- Cerebellum: It controls the balance and posture of the body.
- Pens varolii - The pons is concered with maintenance of normal rhythm of respiration.
- Medulla oblongata - Medullary centres (reflex centres) are present for controlling the functions of important organs, e.g., cardiac centres (heart), respiratory centre, vasomotor centre (for regulating diameter of blood vessels) and reflex centres (for swallowing, vomiting, peristalsis, secretion and activity of alimentary canal, salivation, coughing etc.)
|
Endocrine Gland |
Hormone |
Principal action |
Disorders |
|
Thyroid |
Thyroxine (\[{{T}_{4}}\]) and Triiodothyronine (\[{{T}_{3}}\]) Calcitonin |
Maintains calcium level normal in the body. Increases rate of metabolism in the body. |
Cretinism, myxoedema goiter |
|
Parathyroid |
Parathormone (PTH) |
Increases plasma calcium |
Parathyroid tetany osteoporosis |
|
Adrenal gland (medulla) |
Adrenaline and Noradrenaline |
Increases heartbeat, blood sugar and also constricts blood vessel |
|
|
Adrenal cortex |
Mineralocorticoids (aldosterone) |
Increases re absorption of sodium and excertion of potassium |
Addison's disease Adrenal virilism |
|
|
Glucocorticoids (cortisol) |
Increases blood sugar and affects carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolism |
Gushing's syndrome |
|
Hypothalamus |
ARH |
Regulates corticotropin secretion |
|
|
TRH |
Thyrotropin secretion |
|
|
|
SRH |
Stimulates secretion of gonadotropins |
|
|
|
(Growth hormone releaing factor) |
Regulates secretion of prolactin |
|
|
|
(Prolactir releasing hormone) and (Prolactin inhibitory hormone) |
Control secretion of MSH |
|
|
|
Pituitary gland anterior lobe |
Pituitary gland anterior lobe |
Stimulates general growth |
Pituitary dwarfism, gigantism, Acromegaly |
|
Prolactin |
Stimulates milk production and secretion |
|
|
|
(Follicle stimulating hormone) |
Stimulates ovarian follicle and spermatogenesis |
|
|
|
(Lutemizing hormone) |
Stimulates corpus luteum and ovulation in females and interstitial cell in males |
|
|
|
(Thyroid stimulating hormone) |
Stimulates thyroid gland to secrete hormones |
|
|
|
Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
Stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids |
|
|
|
Intermediate lobe |
Melanocyte stimulating hormone |
Growth and development of melanocyte |
|
|
Posterior lobe |
Oxytocin |
Contraction of uterine muscles and mammary gland cells |
|
|
|
Vasopressin (ADH) |
Promotes re absorption of water from collecting ducts of kidneys |
Diabetes insipidus |
ENDOCRINE PANCREATIC SECRETIONS:
|
|
NAME OF THE CELLS |
PRODUCT |
FUNCTION |
|
1. |
Beta (\[\beta \]) cells |
Insulin and Amylin |
Lower blood sugar level. |
|
2. |
Alpha (\[\alpha \]) cells |
Glucagon |
Raise blood sugar level. |
Function: Produces a group of hormones called androgens mainly testosterone.
Functions: Ovary produces one ovum during each menstrual cycle. It produces 2 groups of steroid hormones called.
(i) Estrogen
(ii) Progesterone
(i) Gametogenesis - Formation of gametes.
(ii) Insemination - Transfer of sperms into female genital tract.
(iii) Fertilisation - Fusion of male and female gametes leading to formation of zygote.
(iv) Implantation - Formation and development of blastocyst and its attachment to the uterine wall.
(v) Gestation - Embryonic development; gestation is the time from conception to birth.
(vi) Parturition - Delivery of baby (the process of birth).
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
