Computer Memory
Category : SSC
Computer Memory
The computer memory is one of the most important elements in a computer system. It stores data and instructions required during the processing of data and output results. Storage may be required for a limited period of time, instantly or for an extended period of time. It also relates to many devices that are responsible for storing data on a temporary or a permanent basis.
Memory Hierarchy
The hierarchical arrangement of storage in current computer architectures is called the memory hierarchy. The computer uses a hierarchy of memory that is organised in a manner to enable the fastest speed and largest capacity of memory as shown in figure.
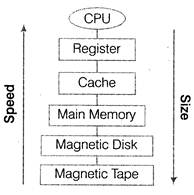
Parameters of Memory
Some related parameters of memory are as follow
(i) Storage Capacity It is representative of the size of memory. The capacity of internal memory and main memory can be expressed in terms of number of words or bytes.
(ii) Access Modes A memory is comprised of various memory locations. The information from these memory locations can be accessed randomly, sequentially and directly.
(iii) Access Time The access time is the time required between the desired modes for a read or write operation till the data is made available or written at the desired location.
(iv) Physical Characteristics In this respect, the devices can be categorised into four main categories as electronic, magnetic, mechanical and optical.
(v) Permanence of Storage Its permanence is high for future use in magnetic materials.
Types of Memory
In general, the memory is classified into two categories as follows
(a) Primary memory or Main memory
(b) Secondary memory or Auxiliary memory
Primary Memory
The memory unit that communicates directly with the CPU is called main memory or the internal memory. The primary memory allows the computer to store data for immediate manipulation and to keep track of what is currently being processed.
It is volatile in nature, it means that when the power is turned OFF, the contents of the primary memory are lost forever. Primary memory can be further classified in two categories which are as follows
Random Access Memory
It is also known as read/write memory that allows CPU to read as well as write data and instructions into it. RAM (Random Access Memory) is used for the temporary storage of input data, output data and intermediate results.
There are two categories of RAM as follows
(a) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) It is made up of memory cells where each cell is composed of one capacitor and one transistor. DRAM must be refreshed continually to store information. DRAM is slower, less expensive and occupies less space on the computer's motherboard.
(b) Static RAM (SRAM) It retains the data as long as power is provided to the memory chip. It needs not be refreshed periodically. SRAM uses multiple transistors for each memory cell. It does not use capacitor. SRAM is often used as cache memory due to its high speed. SRAM is more expensive than DRAM.
|
Cache Memory It is a storage buffer that stores the data winch is used more often, temporarily and makes them available to CPU at a fast rate. Cache memory is a very high speed memory placed in between RAM and CPU. It increases the speed of processing. Cache memory is very expensive, so it is smaller in size. Generally, computers have cache memory, of sizes 256 KB to 2 MB. |
Read Only Memory
It is also known as non-volatile memory or permanent storage. It does not lose its content when the power is switched OFF. ROM (Read Only Memory) has only read capability, no write capability.
ROM can have data and instructions written to it only one time. Once a ROM chip is programmed at the time of manufacturing, it cannot be reprogrammed or rewritten.
There are three categories of ROM as follow
(a) Programmable ROM (FROM) It is also non-volatile in nature. Once a PROM has been programmed, its contents can never be changed. It is one-time programmable device. PROMs are manufactured blank and can be programmed at buffer, final test or in system.
These types of memories are found in video game consoles, mobile phones, implantable medical devices and high definition multimedia interfaces.
(b) Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM) It is similar to PROM, but it can be erased by exposure to strong ultraviolet light, then rewritten.
So, it is also known as Ultraviolet Erasable Programmable ROM (UVEPROM).
(c) Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM (EEPROM) It is similar to EPROM, but it can be erased electrically, then rewritten electrically and the burning process is reversible by exposure to electric pulses. It is the most flexible type of ROM, and is now commonly used for holding BIOS.
Tit - Bits
Secondary Memory
This memory stores much larger amounts of data and information for extended periods of time. Data in secondary memory cannot be processed directly by the CPU, it must first be copied into primary storage, i.e. RAM.
Secondary storage is used to store data and programs when they are not being processed. It is also non-volatile in nature. Due to this, the data remain in the secondary storage as long as it is not overwritten or deleted by the user. It is a permanent storage, i.e. device.
Secondary memory devices include as follows
|
Magnetic Storage |
· Hard Disk Drive |
|
· Floppy Disk |
|
|
· Magnetic Tape |
|
|
Optical Storage |
· CD |
|
· DVD |
|
|
· Blu-ray Disk |
|
|
Solid State Storage |
· Pen/Flash Drive |
|
· Memory card |
Hard Disk Drive (HDD)
It is a non-volatile, random access digital data storage device. HDD is a data storage device used for storing and retrieving digital information using rotating disks (platters) coated with magnetic material. All programs of a computer are installed in hard disk.
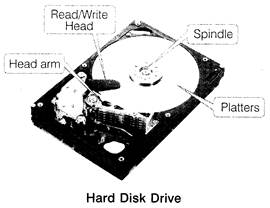
It consists of a spindle that holds non-magnetic flat circular disks, called platters, which hold the recorded data. Each platter requires two read/write heads that are used to write and read the information from a platter.
All the read/write heads are attached to a single access arm so that they cannot move independently.

The information is recorded in bands; each band of information is called a track. Each platter has the same number of tracks and a track location that cuts across all platters is called a cylinder.
The tracks are divided into pie-shaped sections known as sectors.
Floppy Disk (Diskette)
It is used to store data but it can store small amount of data and it is slower to access than hard disks. Floppy disk round in shape and a thin plastic disk coated with iron oxide. Data is retrieved or recorded on the surface of the disk through a slot on the envelope. Floppy disk is removable from the drive. Floppy disk is available in three sizes; 8 inch, \[5\frac{1}{4}\] inch and \[3\frac{1}{2}\]inch.
Magnetic Tape
These tapes are made of a plastic film-type material coated with magnetic materials to store data permanently. Data can be read as well as recorded. It is usually 12.5 mm to 25 mm wide and 500 m to 1200 m long. These can store data in a sequential manner.
The data stored in magnetic tape is in the form of tiny segments of magnetised and demagnetized portion on the surface of the material. Magnetic tapes are durable, can be written, erased and re-written. Magnetic tapes hold the maximum data, which can be accessed sequentially.
Compact Disk
It is the most popular and the least expensive type of optical disk. A CD (Compact Disk) is capable of being used as a data storage device along with storing of digital audio. The files are stored on this particular contiguous sectors.
CDs are categorised into three main types as follow
(a) CD-ROM (Compact Disk-Read Only Memory)
(b) CD-R (Compact Disk- Recordable)
(c) CD-RW (Compact Disk- Rewritable)
Digital Video Disk
DVD is also known as Super Density Disk (SDD) or Digital Versatile Disk (DVD). A DVD (Digital Video Disk) is an optical disk storage media manufactured by Philips, Sony, Toshiba and Panasonic in 1995. DVDs offer higher storage capacity than compact disks while having the same dimensions.
Depending upon the disk type, DVD can store several Gigabytes of data (4.7 GB-17.08 GB). DVDs are primarily used to store music or 6 movies and can be played back on your television or the computer too. They are not rewritable media.
DVDs come in three varieties as follows
(a) DVD--ROM
(Digital Video Disk-Read Only Memory)
(b) DVD-R (DVD-Recordable)
(c) DVD-RW (DVD-Rewntable)
Tit-Bits
Hard disk is a fixed disk. i.e. cannot be removed from the drive.
Blu-ray Disk
It is an optical disk storage medium designed to recapture the data normally in DVD format. Blu-ray disks (BD) contain 25 GB (23.31 GB) per layer space. The name Blu-ray disk refers to the blue laser used to read the disk, which allows information to be stored at a greater density than the longer- wavelength red laser used in DVDs. Blu-ray can hold almost 5 times more data than a single layer DVD.
The variations in the formats are as follows
(a) BD-ROM (Read only)
(b) BD-R (Recordable)
(c) BD-RW (Rewritable)
(d) BD-RE (Rewritable)
Pen/Thumb Drive
Pen drive is also known as flash drive. A flash drive is a data storage device that consists of flash memory (key memory) with a portable USB (Universal Serial Bus) interface. USB flash drives are typically removable, rewritable and much smaller than a floppy disk.
Today, flash drives are available in various storage capacities as 256MB, 512MB, 1GB, 4GB, 16GB upto 64 GB. They are widely used as an easy and small medium to transfer and store the information from their computer.
Memory Cards
These are the data storage devices in a clip shaped which can store the data in it. They are commonly used in many electronic devices, including digital cameras, mobile phones, laptop computers.
They are small, re-recordable, easily portable and very light weighted.
Secondary Memory Device and their Storage Method and Capacity
|
Secondary Memory Device |
Storage Method |
Capacity |
|
Floppy Disk (5.25 inch) |
Magnetic |
1.2 MB |
|
Floppy Disk (3.5 inch) |
Magnetic |
1.44MB |
|
Floppy Disk (8 inch) |
Magnetic |
80 KB to 242 KB |
|
CD-ROM |
Optical |
640 MB to 680 MB |
|
DVD-ROM |
Optical |
4.7 GB to 17 GB |
|
Pen Drive |
Solid State |
1GB to 512GB |
|
Magnetic Tape |
Magnetic |
upto 1 TB |
Basic Units of Memory Measurements
|
1 Bit |
Binary Digit (o or l) |
|
8 Bits |
1 Byte =2 Nibble |
|
1024 Bytes |
1 KB (KiloByte) |
|
1024 KB |
1 MB (MegaByte) |
|
1024MB |
1 GB(Giga Byte) |
|
1024 GB |
1 TB(Tera Byte) |
|
1024 TB |
1 PB(Peta Byte) |
|
1024 PB |
1 EB(Exa Byte) |
|
1024 EB |
1 ZB(Zetta Byte) |
|
1024 ZB |
1 YB (Yotta Byte) |
|
1024 YB |
1 (Bronto Byte) |
|
1024 Brontobyte |
1 (Geop Byte) |
Note Bit is the smallest memory measurement unit. Geop Byte is the highest memory measurement unit.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
