NCERT Extracts - The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
Category : UPSC
Early Theories of the Origin of the Earth
- A large number of hypotheses were put forth by different philosophers and scientists regarding the origin of the earth.
- One of the earlier and popular arguments was by German philosopher Immanuel Kant. Mathematician Laplace revised it in 1796.
- It is known as Nebular Hypothesis. The hypothesis considered that the planets were formed out of a cloud of material associated with a youthful sun, which was slowly rotating.
- Later in 1900, Chamberlain and Moulton considered that a wandering star approached the sun.
- As a result, a cigar-shaped extension of material was separated from the solar surface.
- As the passing star moved away, the material separated from the solar surface continued to revolve around the sun and it slowly condensed into planets.
- Sir James Jeans and later Sir Harold Jeffrey supported this argument.
- At a later date, the arguments considered of a companion to the sun to have been coexisting.
- These arguments are called binary theories. In 1950, Otto Schmidt in Russia and Carl Weizascar in Germany somewhat revised the 'nebular hypothesis', though differing in details.
- They considered that the sun was surrounded by solar nebula containing mostly the hydrogen and helium along with what may be termed as dust.
- The friction and collision of particles led to formation of a disk-shaped cloud and the planets were formed through the process of accretion.
- However, scientists in later period took up the problems of origin of universe rather than that of just the earth or the planets.
Modem Theories of the Origin of the Universe
- The most popular argument regarding the origin of the universe is the Big Bang Theory. It is also called expanding universe hypothesis.
- Edwin Hubble, in 1920, provided evidence that the universe is expanding.
- As time passes, galaxies move further and further apart. Similarly, the distance between the galaxies is also found to be increasing and thereby, the universe is considered to be expanding.
- Scientists believe that though the space between the galaxies is increasing, observations do not support the expansion of galaxies.
- The Big Bang Theory considers the following stages in the development of the universe
- In the beginning, all matter forming the universe existed in one place m the form of a “tiny ball” (singular atom) with an unimaginably small volume, infinite temperature and infinite density.
- At the Big Bang the “tiny ball” exploded violently. This led to a huge expansion. It is now generally accepted that the event of big bang took 13.7 billion years before the present.
- The expansion continues even to the present day. As it grew, some energy was converted into matter.
- There was particularly rapid expansion within fractions of a second after the bang.
- Thereafter, the expansion has slowed down. Within first three minutes from the Big Bang event, the first atom began to form.
- Within 3,00,000 years from the Big Bang, temperature dropped to 4,500 K (Kelvin) and gave rise to atomic matter. The universe became transparent.
- The expansion of universe means increase in space between the galaxies.
- An alternative to this was Hoyle's concept of steady state.
- It considered the universe to be roughly the same at any point of time.
- However, with greater evidence becoming available about the expanding universe, scientific community at present favours argument of expanding universe.
The Star Formation
²
- The distribution of matter and energy was not even in the early universe.
- These initial density differences gave rise to differences in gravitational forces and it caused the matter to get drawn together.
- These formed the bases for development of galaxies. A galaxy contains a large number of stars.
- Galaxies spread over vast distances that are measured in thousands of light-years.
- The diameters of individual galaxies range from 80,000-1,50,000 light years. :
- A galaxy starts to form by accumulation of hydrogen gas in the form of a very large cloud called nebula.
- Eventually, growing nebula develops localised clumps of gas. These clumps continue to grow into even denser gaseous bodies, giving rise to formation of stars.
- The formation of stars is believed to have taken place some 5-6 billion years ago.
- A light year is a measure of distance and not of time. Light travels at a speed of 3,00,000 km/second.
- Considering this, the distances the light will travel in one year is taken to be one light year. This equals to 9.4611012 km.
Formation of Planets
- The following are considered to be the stages in the development of planets :
- The stars are localised lumps of gas within a nebula.
- The gravitational force within the lumps leads to the formation of a core to the gas cloud and a huge rotating disc of gas and dust develops around the gas core.
- In the next stage, the gas cloud starts getting condensed and the matter around the core develops into small-rounded objects.
- These small-rounded objects by the process of cohesion develop into what is called planetesimals.
- Larger bodies start forming by collision, and gravitational attraction causes the material to stick together. Planetesimals are a large number of smaller bodies.
- In the final stage, these large number of small planetesimals accrete to form a fewer large bodies in the form of planets.
Our Solar System
- Our Solar system consists of eight planets.
- The nebula from which our Solar system is supposed to have been formed, started its collapse and core formation some time 5-5.6 billion years ago and the planets were formed about 4.6 billion years ago.
- Our solar system consists of the sun (the star), 8 planets, 63 moons, millions of smaller bodies like asteroids and comets and huge quantity of dust-grains and gases.
- Out of the eight planets, mercury, venus, earth and mars are called as the inner planets as they lie between the sun and the belt of asteroids the other four planets are called the outer planets.
- Alternatively, the first four are called Terrestrial, meaning earth-like as they are made up of rock and metals, and have relatively high densities.
- The rest four are called Jovian or Gas Giant planets.
- Jovian means Jupiter-like.
- Most of them are much larger than the terrestrial planets and have thick atmosphere, mostly of helium and hydrogen.
- All the planets were formed in the same period sometime about 4.6 billion years ago.
- Till recently (August, 2006), Pluto was also considered a planet. However, in a meeting of the International Astronomical Union, a decision was taken that Pluto like other celestial objects (2003 UB^) discovered in recent past may be called 'dwarf planet'.
- The inner planets rocky while others are mostly in gaseous form.
- The difference between terrestrial and jovian planets can be attributed to the following conditions:
- The terrestrial planets were formed in the close vicinity of the parent star where it was too warm for gases to condense to solid particles.
- Jovian planets were formed at quite a distant location.
- The solar wind was most intense nearer the sun; so, it blew off lots of gas and dust from the terrestrial planets.
- The solar winds were not all that intense to cause similar removal of gases from the Jovian planets.
- The terrestrial planets are smaller and their lower gravity could not hold the escaping gases.
The Moon
- He moon is the only natural satellite of the earth. Like the origin of the earth, there have been attempts to explain how the moon was formed.
- In 1838, Sir George Darwin suggested that initially, the earth and the moon formed a single rapidly rotating body.
- The whole mass became a dumb-bell-shaped body and eventually it broke.
- It was also suggested that the material forming the moon was separated from what we have at present the depression occupied by the Pacific Ocean.
- However, the present scientists do not accept either of the explanations.
- It is now generally believed that the formation of moon, as a satellite of the earth, is an outcome of 'giant impact' or what is described as "the big splat".
- A body of the size of one to three times that of mars collided into the earth sometime shortly after the earth was formed.
- It blasted a large part of the earth into space.
- This portion of blasted material then continued to orbit the earth and eventually formed into the present moon about 4.44 billion years ago.
Evolution of the Earth
- The planet earth initially was a barren, rocky and hot object with a thin atmosphere of hydrogen and helium.
- This is far from the present day picture of the earth.
- The earth has a layered structure. From the outermost end of the atmosphere to the centre of the earth, the material that exists is not uniform.
- The atmospheric matter has the least density.
- From me surface to deeper depths, the earth's interior has different zones and each of these contains materials with different characteristics.
Evolution of Lithosphere
- The earth was mostly in a volatile state during its primordial stage.
- Due to gradual increase in density the temperature inside has increased.
- As a result the material inside started getting separated depending on their densities.
- This allowed heavier materials (like iron) to sink towards the centre of the earth and the lighter ones to move towards the surface.
- With passage of time it cooled further and solidified and condensed into a smaller size.
- This later led to the development of the outer surface in the form of a crust.
- During the formation of the moon, due to the giant impact, me earth was further heated up.
- It is through me process of differentiation that the earth forming material got separate into different layers.
- Starting from the surface to the central parts, we have layers like the crust, mantle, outer core and inner core.
- From the crust to the core, the density of the material increases.
Evolution of Atmosphere and Hydrosphere
- The present composition of earth's atmosphere is chiefly contributed by nitrogen and oxygen.
- There are three stages in the evolution of the present atmosphere. The first stage is marked by the loss of primordial atmosphere.
- In the second stage, the hot interior of the earth contributed to the evolution of the atmosphere.
- Finally, the composition of the atmosphere was modified by the living world through the process of photosynthesis.
- The early atmosphere, with hydrogen and helium, is supposed to have been stripped off as a result of the solar winds.
- This happened not only in case of the earth, but also in all the terrestrial planets, which were supposed to have lost their primordial atmosphere through the impact of solar winds.
- During the cooling of the earth, gases and water vapour were released from the interior solid earth.
- This started the evolution of the present atmosphere.
- The early atmosphere largely contained water vapour, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia and very little of free oxygen.
- The process through which the gases were outpoured from the interior is called degassing.
- Continuous volcanic eruptions contributed water vapour and gases to the atmosphere.
- As the earth cooled, the water vapour released started getting condensed.
- The carbon dioxide in the atmosphere got dissolved in rainwater and the temperature further decreased causing more condensation and more rains.
- The rainwater falling onto the surface got collected in the depressions to give rise to oceans.
- The earth's oceans were formed within 500 million years from the formation of the earth.
- This tells us that the oceans are as old as 4,000 million years. Sometime around 3,800 million years ago, life began to evolve.
- However, around 2,500-3,000 million years before the present, the process of photosynthesis got evolved.
- Life was confined to the oceans for a long time.
- Oceans began to have the contribution of oxygen through the process of photosynthesis.
- Eventually, oceans were saturated with oxygen, and 2,000 million years ago, oxygen began to flood the atmosphere.
Origin of Life
- The last phase in the evolution of the earth relates to the origin and evolution of life.
- Modem scientists refer to the origin of life as a kind of chemical reaction, which first generated complex organic molecules and assembled them.
- This assemblage was such that they could duplicate themselves converting inanimate matter into living substance.
- It can be assumed mat life began to evolve sometime 3.800 million years ago
Latitudes and Longitudes

Latitude
- All paralled circles from the -equator up to the poles are called parallels of latitudes. Latitudes are measured in degrees. The equator represents the zero degree latitude.
- 90 degrees north latitude marks the North Pole and 90 degrees south latitude marks the South Pole.
- All parallels north of the equator are called 'north latitudes.' Similarly all paralles south of the equator are called 'south latitudes.'
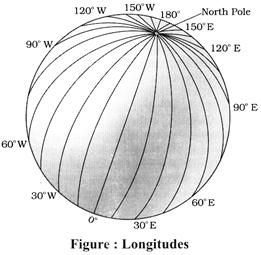
Longitudes
- To fix the position of a place, it is necessary to know something more than the latitude of that place.
- In order to locate a place, we must find out how far east or west places are from a given line of reference running from the North Pole to the South Pole.
- These lines of references are called the meridians of longitude, and the distance between them are measured in 'degrees of longitude.' Each degree is further divided into minutes, and minutes into seconds.
- They are semi-circles and the distance between them decreases steadily polewards untill it becomes zero at the poles, where all the meridians meet.
- Unlike parallels of latitude, all meridians are of equal length. Thus, it was difficult to number the meridians. Hence, all countries decided that the count should begin from the meridian which passed through Greenwich, where the British Royal Observatory is located.
- This meridian is called the Prime Meridian. Its value is 0° longitude and from it we count 180° eastward as well as 180° westward.
- The Prime Meridian and 180° meridian divide the earth into two equal halves, the Eastern Hemisphere and the Western Hemisphere.
- 180° East and 180° West meridians are on the same line.
- In India, the longitude ofis treated as the standard meridian. The local time at this meridian is taken as the standard time for the whole country. It is known as the Indian Standard Time (1ST).
- India located east of Greenwich at 82°30'E in 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of GMT. So it will be 7:30 p.m. in India when it is 2:00 p.m. noon in London.
- Some countries have a great longitudinal extent and so they have adopted more than one standard time. For example, in Russia, there are as many as eleven standard times.
- The earth has been divided into twenty-four time zones of one hour each. Each zone thus covers 15° of longitude.
Axis
- A needle is fixed through me globe in a tilted manner, which is called its axis. Two points on the globe through which the needle passes are two poles - North Pole and South Pole.
- The real earth ha no such needle. It moves around its axis, which is an imaginary line.
Equator
- Another imaginary line running on the globe divides it into two equal parts. This line is known as the equator. The northern half of the earth is known as the Northern Hemisphere and the southern half is known as the Southern Hemisphere.
Important Parallels of Latitudes
- There are four important parallels of latitudes :
- Tropic of Cancer \[(23{{{}^{1}/{}_{2}}^{o}}N)\]in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Tropic of Capricorn \[(23{{{}^{1}/{}_{2}}^{o}}S)\] in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Arctic Circle of \[66{{{}^{1}/{}_{2}}^{o}}\] north of the equator.
- Antarctic Circle at 66'/2° south of the equator.
Heat Zones of the Earth
- The mid-day sun is exactly overhead at least once a year on all latitudes in between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn. This area, therefore, receives the maximum heat and is called the Torrid Zone.
- The areas bounded by the Tropic of Cancer and the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere, and the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere, have moderate temperatures. These are, therefore, called Temperate Zones.
- Areas lying between the Arctic Circle and the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle and Hemisphere, are very cold.
- It is because here the sun does not rise much above the horizon. Therefore, if rays are always slanting and provide less heat. These are, therefore, called Frigid Zones (very cold).
Some Important Facts
- While watching the night sky, you may notice various patterns formed by different groups of stars. These are called constellations. Ursa Major or Big Bear is one such constellation.
- One of the most easily recognisable constellation is the small bear or Saptarishi (Sapta- seven, rishi-sages). It is a group of seven stars. ,
- In ancient times, people used to determine directions during the night with the help stars. The North star indicates the north direction. It is also called the Pole Star.
- It always remains in the same position in the sky. We can locate the position of the Po Star with the help of the Saptarishi.
- The sun, eight planets, satellites and some other celestial bodies known as asteroids and meteoroids form the solar system. We often call it a solar family, with the sun as its Head.
- The sun is in the centre of the solar system. It is huge and made up of extremely hot gases. It provides the pulling force that binds the solar system. The sun is the ultimate source of heat and light for the solar system. The sun is about 150 million km away from the earth.
- There are eight planets in our solar system. All the eight planets of the solar system move around the sun in fixed paths. These paths are elongated. They are called orbits.
- Mercury is nearest to the sun. It takes only about 88 days to complete one round along its orbit.
- Venus is considered as 'Earth's-twin' because its size and shape are very much similar to that of the earth.
- In Size, it is the fifth largest planet. It is slightly flattened at the poles. That is why, shape is described as a Geoid. Geoid means an earth-like shape.
- From the outer space, the earth appears blue because its two-thirds surface is coven by water. It is, therefore, called a blue planet.
- Our earth has only one satellite, that is, the moon. Its diametre is only one-quarter that of the earth. It is about 3,84,400 km away from us.
- The moon moves around the earth in about 27 days. It takes exactly the same time complete one spin. As a result, only one side of the moon is visible to us on the earth Q Neil Armstrong was the first man to step on the surface of the moon on 21 July, 1969.
- A Satellite is a celestial body that moves around the planets in me same way as the planets move around the sun.
- A Human-made Satellite is an artificial body. It is designed by scientists to gather information about the universe or for communication.
- It is carried by a rocket and placed in the orbit around the earth. Some of the Indian satellites in space are INSAT, IRS, EDUSAT, etc.
- Apart from the stars, planets and satellites, there are numerous tiny bodies which also move around the sun. These bodies are called asteroids. They are found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
- The small pieces of rocks which move around the sun are called meteoroids Q A galaxy is a huge system of billions of stars, and clouds of dust and gases. There are millions of such galaxies that make the Universe.
- Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus have rings around them. These are belts of small debris These nngs may be seen from the earth with the help of powerful telescopes
- 'Sol’ in Roman mythology is the 'Sungod'. 'Solar' means -related to the sun'. The family of the sun is, therefore, called the solar system. Geography is an English word It has its origin m Greek, which relates to the description of the earth. It is made of two Greek words, 'ge’ meaning' 'earth- and 'graphia' meaning 'writing'. The light of the sun takes about eight minutes to reach the earth.

