Answer:
(i) (a) Ionic compounds have strong force
of attraction between the oppositely charged ions (e.g., Na+ and Cl-),
so they are solids. Covalent compounds have weak force of attraction between
their molecules, so they are usually liquids or gases.
(b)
Ionic compounds are soluble in water but covalent compounds are insoluble in
water.
(c)
Ionic compounds conduct electricity when dissolved in water or when melted
because they contain ions (charged particles). But, covalent compounds like glucose
do not conduct electricity because they do not contain ions.
(ii)
(a) The metal M which is in the middle of the reactivity series (such as iron,
zinc, lead, copper, etc.) is moderately reactive. So, for obtaining such metals
from their compounds, their sulphides and carbonates (in which they are present
in nature) are first converted into their oxides by the process of roasting and
calcination respectively.
For example,
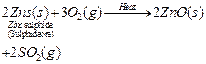
![]() The
metal oxides (MO) are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using
suitable reducing agents such as carbon. For example, zinc metal from its oxide
is obtained as follow:
ZnO(s) + C(s) ® Zn(s) + CO(g)
Zinc oxide Zinc
(b)The metal N which is high up in the reactivity series
(such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, aluminium, etc.), is very reactive and
cannot be obtained from its compound by heating with carbon.
Therefore, such metals are obtained by electrolytic
reduction of their molten salt. For example, sodium is obtained by the
electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (Nacl).
At cathode: Na++e- ® Na
At anode: 2Cl ® Cl2
+ 2e-
The
metal oxides (MO) are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using
suitable reducing agents such as carbon. For example, zinc metal from its oxide
is obtained as follow:
ZnO(s) + C(s) ® Zn(s) + CO(g)
Zinc oxide Zinc
(b)The metal N which is high up in the reactivity series
(such as sodium, magnesium, calcium, aluminium, etc.), is very reactive and
cannot be obtained from its compound by heating with carbon.
Therefore, such metals are obtained by electrolytic
reduction of their molten salt. For example, sodium is obtained by the
electrolysis of molten sodium chloride (Nacl).
At cathode: Na++e- ® Na
At anode: 2Cl ® Cl2
+ 2e-
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
