-
question_answer1)
A 1mA beam of protons with a cross-sectional area of 0.5 sq. mm is moving with a velocity of \[3\times {{10}^{4}}m{{s}^{-1}}\]. Then charge density of beam is [CPMT 2002]
A)
\[6.6\times {{10}^{-4}}C/{{m}^{3}}\] done
clear
B)
\[6.6\times {{10}^{-5}}C/{{m}^{3}}\] done
clear
C)
\[6.6\times {{10}^{-6}}C/{{m}^{3}}\] done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
A particle of mass M at rest decays into two particles of masses m1 and m2, having non-zero velocities. The ratio of the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particles, \[{{\lambda }_{1}}/{{\lambda }_{2}}\]is [IIT-JEE 1999; KCET 2003]
A)
\[{{m}_{1}}/{{m}_{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{m}_{2}}/{{m}_{1}}\] done
clear
C)
1.0 done
clear
D)
\[\sqrt{{{m}_{2}}}/\sqrt{{{m}_{1}}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
A photon and an electron have equal energy E. \[{{\lambda }_{\text{photon}}}/{{\lambda }_{\text{electron}}}\] is proportional to [UPSEAT 2003; IIT-JEE (Screening) 2004]
A)
\[\sqrt{E}\] done
clear
B)
\[1/\sqrt{E}\] done
clear
C)
\[1/E\] done
clear
D)
Does not depend upon E done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
When photon of energy 4.25 eV strike the surface of a metal A, the ejected photoelectrons have maximum kinetic energy TA eV and de-Brolie wavelength \[{{\lambda }_{A}}\]. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons liberated from another metal B by photon of energy 4.70 eV is \[{{T}_{B}}=({{T}_{A}}-1.50)\ eV\]. If the de-Broglie wavelength of these photoelectrons is \[{{\lambda }_{B}}=2{{\lambda }_{A}}\], then [IIT-JEE 1994]
A)
The work function of A is 2.25 eV done
clear
B)
The work function of B is 4.20 eV done
clear
C)
\[{{T}_{A}}=2.00\ eV\] done
clear
D)
\[{{T}_{B}}=2.75\ eV\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer5)
An image of the sun is formed by a lens of focal length of 30 cm on the metal surface of a photoelectric cell and a photoelectric current I is produced. The lens forming the image is then replaced by another of the same diameter but of focal length 15 cm. The photoelectric current in this case is [Manipal MEE 1995]
A)
\[\frac{I}{2}\] done
clear
B)
I done
clear
C)
2I done
clear
D)
4I done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
When an inert gas is filled in the place vacuum in a photo cell, then [MP PMT 1997]
A)
Photo-electric current is decreased done
clear
B)
Photo-electric current is increased done
clear
C)
Photo-electric current remains the same done
clear
D)
Decrease or increase in photo-electric current does not depend upon the gas filled done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer7)
A photon of \[1.7\times {{10}^{-13}}\]Joules is absorbed by a material under special circumstances. The correct statement is [MP PET 1999; JIPMER 2000]
A)
Electrons of the atom of absorbed material will go the higher energy states done
clear
B)
Electron and positron pair will be created done
clear
C)
Only positron will be produced done
clear
D)
Photoelectric effect will occur and electron will be produced done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
The maximum velocity of an electron emitted by light of wavelength \[\lambda \] incident on the surface of a metal of work function \[\varphi ,\] is [MP PMT/PET 1998, MP PMT 2003]
A)
\[{{\left[ \frac{2(hc+\lambda \varphi )}{m\lambda } \right]}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{2(hc-\lambda \varphi )}{m}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{\left[ \frac{2(hc-\lambda \varphi )}{m\lambda } \right]}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{\left[ \frac{2(h\lambda -\varphi )}{m} \right]}^{1/2}}\] Where h = Planck's constant, m = mass of electron and c = speed of light. done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer9)
When a point source of monochromatic light is at a distance of 0.2 m from a photoelectric cell, the cut-off voltage and the saturation current are 0.6 volt and 18 mA respectively. If the same source is placed 0.6 m away from the photoelectric cell, then [IIT JEE 1992; MP PMT 1999]
A)
The stopping potential will be 0.2 V done
clear
B)
The stopping potential will be 0.6 V done
clear
C)
The saturation current will be 6 mA done
clear
D)
The saturation current will be 18 mA done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
In a photoemissive cell with executing wavelength \[\lambda \], the fastest electron has speed v. If the exciting wavelength is changed to \[3\lambda /4\], the speed of the fastest emitted electron will be [CBSE PMT 1998]
A)
\[v\ {{(3/4)}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[v\ {{(4/3)}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
C)
Less than \[v\ {{(4/3)}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
D)
Greater than \[v\ {{(4/3)}^{1/2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
Ultraviolet light of wavelength 300 nm and intensity 1.0 watt/m2 falls on the surface of a photosensitive material. If 1% of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, then the number of photoelectrons emitted from an area of 1.0 cm2 of the surface is nearly [AMU 1995]
A)
\[9.61\times {{10}^{14}}per\ \sec \]per sec done
clear
B)
\[4.12\times {{10}^{13}}per\ \sec \] per sec done
clear
C)
\[1.51\times {{10}^{12}}per\ \sec \] per sec done
clear
D)
\[2.13\times {{10}^{11}}per\ \sec \] per sec done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer12)
Photoelectric emission is observed from a metallic surface for frequencies \[{{\nu }_{1}}\] and \[{{\nu }_{2}}\] of the incident light rays \[({{\nu }_{1}}>{{\nu }_{2}})\]. If the maximum values of kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted in the two cases are in the ratio of \[1:k\], then the threshold frequency of the metallic surface is [EAMCET (Engg.) 2001]
A)
\[\frac{{{\nu }_{1}}-{{\nu }_{2}}}{k-1}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{k{{\nu }_{1}}-{{\nu }_{2}}}{k-1}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{k{{\nu }_{2}}-{{\nu }_{1}}}{k-1}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{{{\nu }_{2}}-{{\nu }_{1}}}{k}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
Light from a hydrogen discharge tube is incident on the cathode of a photoelectric cell the work function of the cathode surface is 4.2 eV. In order to reduce the photo-current to zero the voltage of the anode relative to the cathode must be made [DCE 2002]
A)
? 4.2 V done
clear
B)
? 9.4 V done
clear
C)
? 17.8 V done
clear
D)
+9.4 V done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
Work function of lithium and copper are respectively 2.3 eV and 4.0 eV. Which one of the metal will be useful for the photoelectric cell working with visible light? (h = 6.6 ´ 10?34 J-s, c = 3 ´ 108 m/s) [DPMT 2003]
A)
Lithium done
clear
B)
Copper done
clear
C)
Both done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
X-rays of wavelength 0.1 Å allowed to fall on a metal get scattered. The wavelength of scattered radiation is 0.111 Å. If h = 6.624 \[\times \]10?34 J-s and m0 = 9 \[\times \]10?31 kg, then the direction of the scattered photons will be
A)
cos?1 (0.547) done
clear
B)
cos?1 (0.4484) done
clear
C)
cos?1 (0.5) done
clear
D)
cos?1 (0.3) done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
The largest distance between the interatomic planes of a crystal is 10-7cm. The upper limit for the wavelength of X-rays which can be usefully studied with this crystal is [CPMT 1984]
A)
1 Å done
clear
B)
2 Å done
clear
C)
10 Å done
clear
D)
20 Å done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
An X-ray tube is operating at 50 kV and 20 mA. The target material of the tube has a mass of 1.0 kg and specific heat 495 J kg-1 \[^{o}{{C}^{-1}}\]. One percent of the supplied electric power is converted into X-rays and the entire remaining energy goes into heating the target. Then [IIT 1995]
A)
A suitable target material must have a high melting temperature done
clear
B)
A suitable target material must have low thermal conductivity done
clear
C)
The average rate of rise of temperature of target would be 2 °C/s done
clear
D)
The minimum wavelength of the X-rays emitted is about \[0.25\times {{10}^{-10}}\,m\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer18)
The wavelength of \[{{K}_{\alpha }}\]X-rays produced by an X-ray tube is 0.76 Å. The atomic number of the anode material of the tube is [IIT 1996]
A)
20 done
clear
B)
60 done
clear
C)
40 done
clear
D)
80 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer19)
X-ray beam of intensity \[{{I}_{0}}\]passes through an absorption plate of thickness d. If absorption coefficient of material of plate is \[\mu \], the correct statement regarding the transmitted intensity I of X-ray is [MP PET 1999]
A)
\[I={{I}_{0}}(1-{{e}^{-\mu d}})\] done
clear
B)
\[I={{I}_{0}}{{e}^{-\mu d}}\] done
clear
C)
\[I={{I}_{0}}(1-{{e}^{-\mu /d}})\] done
clear
D)
\[I={{I}_{0}}{{e}^{-\mu /d}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer20)
The \[{{K}_{\alpha }}\]X-ray emission line of tungsten occurs at \[\lambda =0.021\]\[nm\]. The energy difference between K and L levels in this atom is about [IIT 1997 Cancelled]
A)
0.51MeV done
clear
B)
1.2 MeV done
clear
C)
59 KeV done
clear
D)
13.6 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
Electrons with energy 80 keV are incident on the tungsten target of an X-ray tube. K shell electrons of tungsten have ionization energy 72.5 keV. X-rays emitted by the tube contain only [IIT-JEE (Screening) 2000]
A)
A continuous X-ray spectrum (Bremsstrahlung) with a minimum wavelength of ~ 0.155Å done
clear
B)
A continuous X-ray spectrum (Bremsstrahlung] with all wavelengths done
clear
C)
The characteristic X-rays spectrum of tungsten done
clear
D)
A continuous X-ray spectrum (Bremsstrahlung) with a minimum wavelength of ~ 0.155Å and the characteristic X-ray spectrum of tungsten done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
The X-ray wavelength of \[{{L}_{\alpha }}\] line of platinum (Z=78) is \[1.30{AA}.\] The X ?ray wavelength of \[{{L}_{\alpha }}\] line of Molybdenum (Z=42) is [EAMCET (Eng.) 2000]
A)
5.41 \[\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
B)
4.20 \[\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
C)
2.70 \[\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
D)
1.35 \[\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
The ratio of de-Broglie wavelengths of molecules of hydrogen and helium which are at temperature 27oC and 127oC respectively is
A)
\[\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
B)
\[\sqrt{\frac{3}{8}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\sqrt{\frac{8}{3}}\] done
clear
D)
1 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
A silver ball of radius 4.8 cm is suspended by a thread in the vacuum chamber. UV light of wavelength 200 nm is incident on the ball for some times during which a total energy of 1 ´ 10?7 J falls on the surface. Assuming on an average one out of 103 photons incident is able to eject electron. The potential on sphere will be
A)
1 V done
clear
B)
2 V done
clear
C)
3 V done
clear
D)
Zero done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
A photon of wavelength 6630 Å is incident on a totally reflecting surface. The momentum delivered by the photon is equal to
A)
6.63 ´ 10?27 kg-m/sec done
clear
B)
2 ´ 10?27 kg-m/sec done
clear
C)
10?27 kg-m/sec done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer26)
The ratio of de-Broglie wavelength of a a-particle to that of a proton being subjected to the same magnetic field so that the radii of their path are equal to each other assuming the field induction vector \[\overrightarrow{B}\] is perpendicular to the velocity vectors of the a-particle and the proton is
A)
1 done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{4}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{2}\] done
clear
D)
2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer27)
Ka wavelength emitted by an atom of atomic number Z = 11 is l. Find the atomic number for an atom that emits Ka radiation with wavelength 4l [IIT-JEE (Screening) 2005]
A)
Z = 6 done
clear
B)
Z = 4 done
clear
C)
Z = 11 done
clear
D)
Z = 44 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer28)
The potential energy of a particle of mass m is given by \[U(x)=\left\{ \begin{align} & {{E}_{0}};\ \ \ 0\le x\le 1 \\ & \,0\ ;\ \ \ \,\,\,\,x>1 \\ \end{align} \right.\]l1 and l2 are the de-Broglie wavelengths of the particle, when 0 £ x £ 1 and x > 1 respectively. If the total energy of particle is 2E0, the ratio \[\frac{{{\lambda }_{1}}}{{{\lambda }_{2}}}\] will be [Based on IIT-JEE (Mains) 2005]
A)
2 done
clear
B)
1 done
clear
C)
\[\sqrt{2}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer29)
Rest mass energy of an electron is 0.51 MeV. If this electron is moving with a velocity 0.8 c (where c is velocity of light in vacuum), then kinetic energy of the electron should be.
A)
0.28 MeV done
clear
B)
0.34 MeV done
clear
C)
0.39 MeV done
clear
D)
0.46 MeV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer30)
A proton, a deutron and an a-particle having the same momentum, enters a region of uniform electric field between the parallel plates of a capacitor. The electric field is perpendicular to the initial path of the particles. Then the ratio of deflections suffered by them is
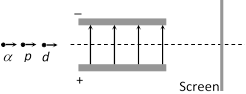
A)
1 : 2 : 8 done
clear
B)
1 : 2 : 4 done
clear
C)
1 : 1 : 2 done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer31)
In order to coincide the parabolas formed by singly ionised ions in one spectrograph and doubly ionized ions in the other Thomson?s mass spectrograph, the electric fields and magnetic fields are kept in the ratios 1 : 2 and 3 : 2 respectively. Then the ratio of masses of the ions is
A)
3 : 4 done
clear
B)
1 : 3 done
clear
C)
9 : 4 done
clear
D)
None of these done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer32)
Let \[{{\lambda }_{\alpha }}\], \[{{\lambda }_{\beta }}\] and \[{{{\lambda }'}_{\alpha }}\] denote the wavelengths of the X-rays of the \[{{K}_{\alpha }},\,{{K}_{\beta }}\] and \[{{L}_{\alpha }}\] lines in the characteristic X-rays for a metal
A)
\[{{\lambda }_{\alpha }}>{{{\lambda }'}_{\alpha }}>{{\lambda }_{\beta }}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{{\lambda }'}_{\alpha }}>{{\lambda }_{\beta }}>{{\lambda }_{\alpha }}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{{{\lambda }_{\beta }}}=\frac{1}{{{\lambda }_{\alpha }}}+\frac{1}{{{{{\lambda }'}}_{\alpha }}}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{1}{{{\lambda }_{\alpha }}}+\frac{1}{{{\lambda }_{\beta }}}=\frac{1}{{{{{\lambda }'}}_{\alpha }}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer33)
The minimum intensity of light to be detected by human eye is \[{{10}^{-10}}W/{{m}^{2}}\]. The number of photons of wavelength \[5.6\times {{10}^{-7}}m\] entering the eye, with pupil area \[{{10}^{-6}}{{m}^{2}}\], per second for vision will be nearly
A)
100 done
clear
B)
200 done
clear
C)
300 done
clear
D)
400 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer34)
In X-ray tube when the accelerating voltage V is halved, the difference between the wavelength of Ka line and minimum wavelength of continuous X-ray spectrum
A)
Remains constant done
clear
B)
Becomes more than two times done
clear
C)
Becomes half done
clear
D)
Becomes less than two times done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer35)
In a photocell bichromatic light of wavelength 2475 Å and 6000 Å are incident on cathode whose work function is 4.8 eV. If a uniform magnetic field of 3 ´ 10?5 Tesla exists parallel to the plate, the radius of the path describe by the photoelectron will be (mass of electron = 9 ´ 10?31 kg)
A)
1 cm done
clear
B)
5 cm done
clear
C)
10 cm done
clear
D)
25 cm done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer36)
Two metallic plates A and B, each of area 5 ´ 10?4m2 are placed parallel to each other at a separation of 1 cm. Plate B carries a positive charge of 33.7 pc. A monochromatic beam of light, with photons of energy 5 eV each, starts falling on plate A at t = 0, so that 1016 photons fall on it per square meter per second. Assume that one photoelectron is emitted for every 106 incident photons. Also assume that all the emitted photoelectrons are collected by plate B and the work function of plate A remains constant at the value 2 eV. Electric field between the plates at the end of 10 seconds is
A)
2 ´ 103 N/C done
clear
B)
103 N/C done
clear
C)
5 ´ 103 N/C done
clear
D)
Zero done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer37)
In the following arrangement y = 1.0 mm, d= 0.24 mm and D = 1.2 m. The work function of the material of the emitter is 2.2 eV. The stopping potential V needed to stop the photo current will be
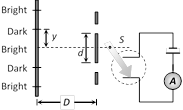
A)
0.9 V done
clear
B)
0.5 V done
clear
C)
0.4 V done
clear
D)
0.1 V done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer38)
The eye can detect 5 ´ 104 photons per square metre per sec of green light (l = 5000 Å) while the ear can detect \[{{10}^{-13}}\,(W/{{m}^{2}})\]. The factor by which the eye is more sensitive as a power detector than the ear is close to
A)
5 done
clear
B)
10 done
clear
C)
106 done
clear
D)
15 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer39)
A photon collides with a stationary hydrogen atom in ground state inelastically. Energy of the colliding photon is 10.2 eV. After a time interval of the order of micro second another photon collides with same hydrogen atom inelastically with an energy of 15 eV. What will be observed by the detector [IIT-JEE (Screening) 2005]
A)
2 photon of energy 10.2 eV done
clear
B)
2 photon of energy of 1.4 eV done
clear
C)
One photon of energy 10.2 eV and an electron of energy 1.4 eV done
clear
D)
One photon of energy 10.2 eV and another photon of 1.4 eV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
