-
question_answer1)
Which of the following statement is true regarding Bohr's model of hydrogen atom?
| (I) Orbiting speed of electrons decreases as it falls to discrete orbits away from the nucleus. |
| (II) Radii of allowed orbits of electrons are proportional to the principal quantum number. |
| (III) Frequency with which electrons orbit around the nucleus in discrete orbits is inversely proportional to the principal quantum number. |
| (IV) Binding force with which the electron is bound to the nucleus increases as it shirts to outer orbits. Select the correct answer using the codes given below: |
A)
I and III done
clear
B)
II and IV done
clear
C)
I, II and III done
clear
D)
II, III and IV done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer2)
The electron in a hydrogen atom makes a transition from an excited state to the ground state. Which of the following statements is true?
A)
Its kinetic energy increases and its potential and total energies decrease done
clear
B)
Its kinetic energy decreases, potential energy increases and its total energy remains the same done
clear
C)
Its kinetic and total energies decrease and it potential energy increases done
clear
D)
Its kinetic, potential and total energies decrease done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer3)
Let \[{{v}_{1}}\] be the frequency of series limit of Lyman series, \[{{v}_{2}}\] the frequency of the first line of Lyman series and \[{{v}_{3}}\] the frequency of series limit of Balmer series. Then which of the following is correct?
A)
\[{{v}_{1}}-{{v}_{2}}={{v}_{3}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{v}_{2}}-{{v}_{1}}={{v}_{3}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{v}_{3}}=\frac{1}{2}({{v}_{1}}+{{v}_{2}})\] done
clear
D)
\[{{v}_{2}}+{{v}_{1}}={{v}_{3}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer4)
In an experiment for positive ray analysis with Thomson method, two identical parabola are obtained when applied electric fields are 3000 and 2000 V/m. The particles are singly ionised particles assuming same magnetic field:
A)
1 : 3 done
clear
B)
2 : 4 done
clear
C)
3 : 1 done
clear
D)
4 : 2 done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer5)
In hydrogen atom, electron makes transition from n =4 to n = 1 level. Recoil momentum of the H atom will be
A)
\[3.4\times {{10}^{-27}}N\text{-}\sec \] done
clear
B)
\[6.8\times {{10}^{-27}}N\text{-}\sec \] done
clear
C)
\[3.4\times {{10}^{-24}}N\text{-}\sec \] done
clear
D)
\[6.8\times {{10}^{-24}}N\text{-}\sec \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer6)
Hydrogen (H), deuterium (4), singly ionized helium (\[H{{e}^{+}}\] and doubly ionized lithium (Li) all have one electroi around the nucleus. Consider n = 2 to n = 1 transition the wavelengths of emitted radiations are \[{{\lambda }_{1}},\]\[{{\lambda }_{2}},\]\[{{\lambda }_{3}},\] and \[{{\lambda }_{4}}\] respectively. Then approximately
A)
\[{{\lambda }_{1}}={{\lambda }_{2}}=4{{\lambda }_{3}}=9{{\lambda }_{4}}\] done
clear
B)
\[4{{\lambda }_{1}}=2{{\lambda }_{2}}=2{{\lambda }_{3}}={{\lambda }_{4}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{\lambda }_{1}}=2{{\lambda }_{2}}=2\sqrt{2}{{\lambda }_{3}}=3\sqrt{2}{{\lambda }_{4}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{\lambda }_{1}}={{\lambda }_{2}}=2{{\lambda }_{3}}=3\sqrt{2}{{\lambda }_{4}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer7)
The number of revolutions per second made by an electroi in the first Bohr orbit of hydrogen atom is of the order of 3
A)
\[{{10}^{20}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{10}^{19}}\] done
clear
C)
\[{{10}^{17}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{10}^{15}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer8)
A gas of H-atoms in excited state \[{{n}_{2}}\] absorbs a photon of some energy and jump in higher energy state \[{{n}_{1}}\] then it returns to ground state after emitting six different wavelengths in emission spectrum. The energy of emitted photon is equal, less or greater than the energy of absorbed photon then \[{{n}_{1}}\] and \[{{n}_{2}}\] will be
A)
\[{{n}_{1}}=5,\,{{n}_{2}}=3\] done
clear
B)
\[{{n}_{1}}=5,\,{{n}_{2}}=2\] done
clear
C)
\[{{n}_{1}}=4,\,{{n}_{2}}=3\] done
clear
D)
\[{{n}_{1}}=4,\,{{n}_{2}}=2\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer9)
The electric potential between a proton and an electron is given by\[V={{V}_{0}}\,In\,\frac{r}{{{r}_{0}}}\], where \[{{r}_{0}}\]is a constant. Assuming Bohr's model to he-applicable, write variation of \[{{r}_{n}}\] with n, n being the principal quantum number
A)
\[{{r}_{n}}\propto n\] done
clear
B)
\[{{r}_{n}}\propto 1/n\] done
clear
C)
\[{{r}_{n}}\propto {{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
D)
\[{{r}_{n}}\propto 1/{{n}^{2}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer10)
The binding energy of deuteron \[\begin{matrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ \end{matrix}H\] is 1.112 Me V pen nucleon and an \[\alpha \]-particle \[\begin{matrix} 4 \\ 2 \\ \end{matrix}He\] has a binding energy of 7.047 Me V per nucleon. Then in the fusion reaction \[\begin{matrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ \end{matrix}He+\begin{matrix} 2 \\ 1 \\ \end{matrix}H\to \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 2 \\ \end{matrix}He+Q\], the energy Q released is
A)
\[1\,MeV\] done
clear
B)
\[11.9\,MeV\] done
clear
C)
\[23.8\,MeV\] done
clear
D)
\[931\,MeV\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer11)
The sun radiates energy in all directions. The average radiations received on the earth surface from the sun is 1 4 kilowatt/\[{{m}^{2}}\]. The average earth- sun distance is \[1.5\times {{10}^{11}}\] meters. The mass lost by the sun per day is (1 day = 86400 seconds)
A)
\[4.4\times {{10}^{9}}\,kg\] done
clear
B)
\[7.6\times {{10}^{14}}\,kg\] done
clear
C)
\[3.8\times {{10}^{12}}\,kg\] done
clear
D)
\[3.8\times {{10}^{14}}\,kg\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer12)
The electron emitted in beta radiation originates from
A)
Inner orbits of atoms done
clear
B)
Free electrons existing in nuclei done
clear
C)
Decay of a neutron in a nucleus done
clear
D)
Photon escaping from the nucleus done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer13)
A sample contains 16g of a radioactive material, the half-life of which is two days. After 32 days, the amount of radioactive material left in the sample is Less than 1 mg
A)
Less than 1 mg done
clear
B)
\[\frac{1}{4}g\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{1}{2}g\] done
clear
D)
\[1g\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer14)
A radioactive substance has a half-life of 60 minutes. After 3 hours, the fraction of atom that have decayed would be
A)
12.5% done
clear
B)
87.5% done
clear
C)
8.5% done
clear
D)
25.1% done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer15)
In a mean life of a radioactive sample
A)
About 1/3 of substance disintegrates. done
clear
B)
About 2/3 of the substance disintegrates done
clear
C)
About 90% of the substance disintegrates done
clear
D)
Almost all the substance disintegrates done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer16)
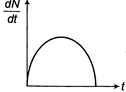
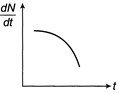
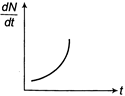
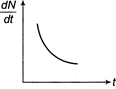
Radioactive element decays to form a stable nuclide, then the rate of decay of reactant \[\left( \frac{dN}{dt} \right)\]will vary with time (t) as shown in figure
A)
B)
C)
D)
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer17)
A star initially has 1040 deuterons. It produces energy via the processes \[_{1}{{H}^{2}}+{}_{1}{{H}^{2}}\to {}_{1}{{H}^{3}}+p\] \[_{1}{{H}^{2}}+{}_{1}{{H}^{3}}\to {}_{2}{{H}^{4}}+n\] The masses of the nuclei are as follows: \[M({{H}^{2}})\] = 2.014 amu; M (p) = 1.007 amu; \[M(n)\] = 1.008 amu; \[M(H{{e}^{4}})\] = 4.001 amu If the average power radiated by the star is \[{{10}^{16}}\]W, the deuteron supply of the star is exhausted in a time of the order of
A)
\[{{10}^{6}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{10}^{8}}\sec \] done
clear
C)
\[{{10}^{12}}\sec \] done
clear
D)
\[{{10}^{16}}\sec \] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer18)
The rate of disintegration was observed to be 1017 disintegrations per sec when its half-life period is 1445 years. The original number of particles are
A)
\[8.9\times {{10}^{27}}\] done
clear
B)
\[6.6\times {{10}^{27}}\] done
clear
C)
\[1.4\times {{10}^{16}}\] done
clear
D)
\[1.2\times {{10}^{17}}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer19)
The radioactivity of sample is \[{{R}_{1}}\] at a time \[{{T}_{1}}\] and \[{{R}_{2}}\] at a time\[{{T}_{2}}\]. If the half-life of the specimen is T, the number of atoms that have disintegrated in the time (\[{{T}_{2}}-{{T}_{1}}\]) is proportional to
A)
\[{{R}_{1}}{{T}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}}{{T}_{2}}\] done
clear
B)
\[{{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{({{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}})}{4}\] done
clear
D)
\[({{R}_{1}}-{{R}_{2}})\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer20)
A nucleus of mass number A, originally at rest, emits an a-particle with speed v. The daughter nucleus recoils with a speed
A)
\[\frac{4v}{A-4}\] done
clear
B)
\[\frac{4v}{A+4}\] done
clear
C)
\[\frac{2v}{A+4}\] done
clear
D)
\[\frac{2v}{A-4}\] done
clear
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer21)
The wavelength of radiation emitted is \[{{\lambda }_{0}}\] when an electron jumps from the third to the second orbit of hydrogen atom. For the electron jump from the fourth to the second orbit of the hydrogen atom, the wavelength of radiation emitted will be\[K{{\lambda }_{0}}\]. Find the value of K.
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer22)
A sodium atom is in one of the states labelled 'Lowest excited levels'. It remains in that state for an average time of \[{{10}^{-8}}\] sec, before it makes a transition back to a ground state. The uncertainty in energy of that excited state is \[M\times {{10}^{-8}}\]eV. Find the value of M
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer23)
A double charged lithium atom is equivalent to hydrogen whose atomic number is 3. The wavelength (in\[\overset{\text{o}}{\mathop{\text{A}}}\,\]) of required radiation for emitting electron from first to third Bohr orbit in \[L{{i}^{++}}\] will be (lonisation energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV) ______.
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer24)
An electron beam accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 5000 V in vacuum is allowed toimpinge on a surface normally. The incident current is \[\mu A\] and if the electrons come to rest on striking the surface the force on it is ______\[\times {{10}^{-8}}N\].
View Solution play_arrow
-
question_answer25)
A and B are two radioactive substances whose half live are 1 and 2 years respectively. Initially 10 gm of A and 1 gm of B is taken. What is the time approximate (in years after which they will have same quantity remaining?
View Solution play_arrow
 done
clear
done
clear
 done
clear
done
clear
 done
clear
done
clear
 done
clear
done
clear
