| A single mutant allele is responsible for the abnormal form of haemoglobin\[(i.e.\text{ }H{{b}^{5}})\]. If it is present in a homozygous state \[(H{{b}^{s}}H{{b}^{s}}),\] person develops sickle-cell anaemia, but if the allele is found in heterozygous state \[(H{{b}^{A}}H{{b}^{S}})\], the person only shows few symptoms for the disease. On the basis of the above situation, work out a cross for a condition in which a woman, who is homozygous for allele marries a male who is heterozygous for the allele? Indicate the probability of having a normal or a diseased child for each of her pregnancies. Also, state the advantage that is conferred by the heterozygous condition of gene \[H{{b}^{S}}\]. |
| Or |
| Haemophilia and colour blindness are sex-linked recessive disorders determined by the alteration or mutation in the single gene. Mention the pattern of inheritance of both disorders in human beings with the help of a cross. |
Answer:
Cross between homozygous female and heterozygous male is as follows 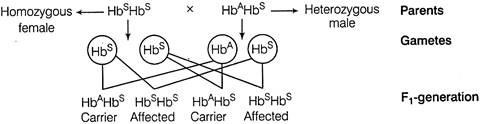
From the cross, it is clear that 50% offsprings are homozygous for the \[H{{b}^{S}}\] allele, whereas 50% are heterozygous for both \[H{{b}^{S}}\] and \[H{{B}^{A}}\]alleles. Above cross, shows that a child has equal probability of developing into a diseased child or with some symptoms of the disease. Therefore, the woman has 50% risk of giving birth to a diseased child, everytime she conceives. The person with heterozygous condition \[(H{{b}^{A}}H{{b}^{S}})\] for sickle-cell anaemia does not develop sickle-cell anaemia and malaria. Due to abnormal shape of haemoglobin, the malarial parasite is not able to survive and complete its life cycle. Hence, in this case, the heterozygous individuals have more chances of survival, which is an advantage with respect to the homozygous individuals. Or Haemophilia, a blood clotting disorder is majorly transmitted from an unaffected carrier female to 50% of the male offsprings. The gene for haemophilia is located on the X-chromosome. The possibility of female becoming haemophilic is extremely rare. Condition I 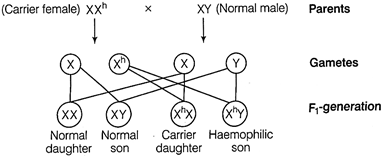
Condition II 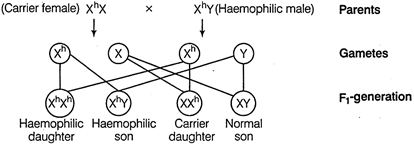
This indicates that for a female to become haemophilia, the gene should be in a homozygous condition, i.e. mother of such female should be carrier and father should be haemophilic. Colour blindness, is the inability to distinguish among some or all colours. In this disorder, mutant forms of genes change the light absorbing capacity of sensory receptors inside the eyes. This trait is mainly common in men, but heterozygous woman may also show symptoms and pass the disorder to some of her sons. Condition I 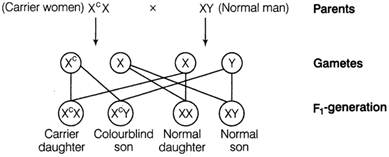
Condition II 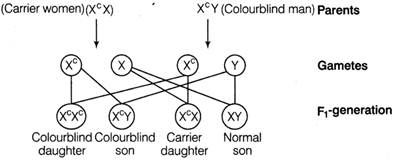
This cross shows that female can be colourblind only in homozygous condition. Both of these disorders show criss - cross inheritance, i.e. transmission of disease occurs from father to daughters and from mother to her sons.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
