Answer:
(i) With increase in the oxidation state of a given transition
metal, the covalent character of its compound increases and thus acidic
character also increases.
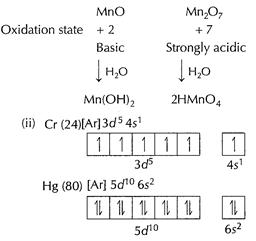 Cr (24) is a hard metal indicating strong interatomic interactions.
This strong interaction is due to valence unpaired electrons in Cr. Greater the
number of unpaired electrons, stronger the interatomic interactions and thus
harder the metal. Hg(80) has very low interatomic interactions due to lack of
unpaired valence electrons and thus is a liquid. [1]
(iii) Transition metals form variety of complexes as
Cr (24) is a hard metal indicating strong interatomic interactions.
This strong interaction is due to valence unpaired electrons in Cr. Greater the
number of unpaired electrons, stronger the interatomic interactions and thus
harder the metal. Hg(80) has very low interatomic interactions due to lack of
unpaired valence electrons and thus is a liquid. [1]
(iii) Transition metals form variety of complexes as
![]() It
is due to
(a) comparatively small size of metal/metal ions
(b) high ionic charge of ions.
(c) availability of vacant d-orbitals for bond formation.
[1]
(iv) Fluorine is the most electronegative element with valency
(-1). It stabilises the highest oxidation state of transition series elements
due to
(a) its highest lattice enthalpy (as in CoF3).
(b) high bond enthalpy due to higher covalent
bonds
It
is due to
(a) comparatively small size of metal/metal ions
(b) high ionic charge of ions.
(c) availability of vacant d-orbitals for bond formation.
[1]
(iv) Fluorine is the most electronegative element with valency
(-1). It stabilises the highest oxidation state of transition series elements
due to
(a) its highest lattice enthalpy (as in CoF3).
(b) high bond enthalpy due to higher covalent
bonds ![]() .
.![]() (maximum oxidation
state of Mn = + 7) is stable due to multiple bonds between Mn and 0. In
(maximum oxidation
state of Mn = + 7) is stable due to multiple bonds between Mn and 0. In ![]() each Mn
is tetrahedral surrounded by O-atoms including Mn?O?Mn
each Mn
is tetrahedral surrounded by O-atoms including Mn?O?Mn
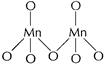 [1]
(v) It is due to much larger third ionisation energy of Mn.
This also explains that + 3 state of Mn is rarely shown in compounds.
[1]
(v) It is due to much larger third ionisation energy of Mn.
This also explains that + 3 state of Mn is rarely shown in compounds.
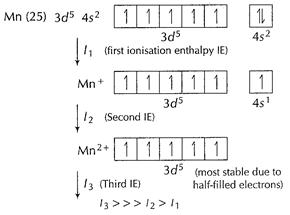 In case of
In case of ![]() and
and![]() stability
of 3d orbitals is low and ionisation is favourable. [1]
Or
(i)
stability
of 3d orbitals is low and ionisation is favourable. [1]
Or
(i) ![]() (thiosulphate)
is oxidised to
(thiosulphate)
is oxidised to ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() (b)
(b) ![]() is
oxidised to
is
oxidised to![]()
![]()
![]() (ii)
(ii)
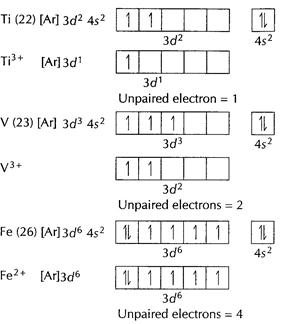
![]()
![]() [Ne]
unpaired electron = 0
Thus,
[Ne]
unpaired electron = 0
Thus,![]() has
maximum number of unpaired electrons. [1]
(a) Zr and Hf, Nb and Ta; and Mo and W have nearly same size.
(b) The elements of 5d-and 4d-transition series resemble
each other than do the elements of 4d-and 5d-series. [1]
(iv) More positive value of reduction potential
indicates more stability of lower oxidation state.
has
maximum number of unpaired electrons. [1]
(a) Zr and Hf, Nb and Ta; and Mo and W have nearly same size.
(b) The elements of 5d-and 4d-transition series resemble
each other than do the elements of 4d-and 5d-series. [1]
(iv) More positive value of reduction potential
indicates more stability of lower oxidation state.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() Thus, stability of+ 2 state is
Thus, stability of+ 2 state is
![]() [1]
(v)
[1]
(v)![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() N =3 (unpaired electrons)
Magnetic moment
N =3 (unpaired electrons)
Magnetic moment ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() [1]
[1]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
