Answer:
The equilibrium level of income or output is that level at which the planned savings and planned investments are equal. It is derived from Aggregate Demand and Aggregate supply approach. Aggregate Demand (AD) in a two sector economy is defined as the sum of Consumption Expenditure [c] and Investment Expenditure (I) i.e. AD=C+I, whereas Aggregate Supply (AS) is defined as the sum of Consumption Expenditure [c] and Saving (S) i.e. AS=C+ S. Mathematically, at equilibrium level of out AD=AS or, C+I=C+S Hence, I=S Or S=I In the graph given, OP is the equilibrium level of income. E is the equilibrium point where Aggregate Demand equals Aggregate Supply Equality between AS and AD implies the equality between S and I. When we extend the line EP vertically downward, it meets at point E? with S and I. It is the equilibrium point of saving and investment approach. OP represents the level of income at which the economy is equilibrium. 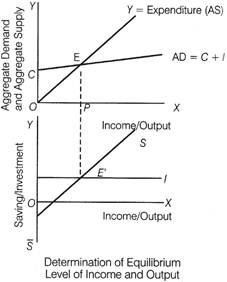
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
