| (i) Demand is perfectly elastic and supply falls. |
| (ii) Supply is perfectly inelastic and demand rises. |
Answer:
Price ceiling refers to the maximum price of a commodity that the sellers can charge from the buyers. It is generally imposed on essential commodities like food grains and certain medicines. 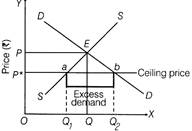 Quantity Demanded / supplied Diagram showing Price Ceiling Implications Government fixes this price lower than the equilibrium market price, so that the concerned commodity remains Within the reach of poorer sections of society. Due to this, following implications of price ceiling are seen: (i) Since ceiling price is lower than the equilibrium price, there is likely to be excess demand in the market, leading to shortage of commodity. (ii) To make extra normal profits, sellers generally resort to black marketing. Or (i) When demand is perfectly elastic and supply decreases, there will be no change in price but the equilibrium quantity will decrease. The following diagram shows that when supply decreases from SS to \[{{S}_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\], equilibrium price remains constant at OP but equilibrium quantity decreases from OQ to\[O{{Q}_{1}}.\]
Quantity Demanded / supplied Diagram showing Price Ceiling Implications Government fixes this price lower than the equilibrium market price, so that the concerned commodity remains Within the reach of poorer sections of society. Due to this, following implications of price ceiling are seen: (i) Since ceiling price is lower than the equilibrium price, there is likely to be excess demand in the market, leading to shortage of commodity. (ii) To make extra normal profits, sellers generally resort to black marketing. Or (i) When demand is perfectly elastic and supply decreases, there will be no change in price but the equilibrium quantity will decrease. The following diagram shows that when supply decreases from SS to \[{{S}_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\], equilibrium price remains constant at OP but equilibrium quantity decreases from OQ to\[O{{Q}_{1}}.\] 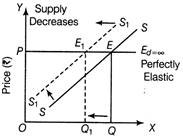 Quantity (units) Demand and Supply Curves (ii) When supply is perfectly inelastic and demand increases, the price of the commodity will increase but the equilibrium quantity of that commodity remains constant. The following diagram shows that when demand increases from DD to\[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\]the equilibrium price also increases from OP to\[O{{P}_{1}}\]but equilibrium quantity of that commodity remains constant at OQ.
Quantity (units) Demand and Supply Curves (ii) When supply is perfectly inelastic and demand increases, the price of the commodity will increase but the equilibrium quantity of that commodity remains constant. The following diagram shows that when demand increases from DD to\[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\]the equilibrium price also increases from OP to\[O{{P}_{1}}\]but equilibrium quantity of that commodity remains constant at OQ. 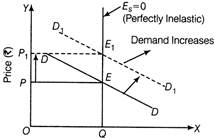 Quantity (units) Demand and Supply Curves
Quantity (units) Demand and Supply Curves
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
