A) \[\sigma \to p\](empty) and \[\sigma \to {{\pi }^{*}}\]electron delocalisations
B) \[\sigma \to {{\sigma }^{*}}\] and \[\sigma \to \pi \]electron delocalisations
C) \[\sigma \to p\](filled) and \[\sigma \to \pi \]electron delocalisations
D) p (filled) \[\to {{\sigma }^{*}}\]and \[\sigma \to {{\pi }^{*}}\]electrons delocalisations
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
| Spreading out charge by the overlap of an empty p-orbital with an adjacent o-bond is called hyperconjugation. This overlap (the hyperconjugation) delocalises the positive charge on the carbocation, spreading it over a larger volume and this stabilizes the carbocation. |
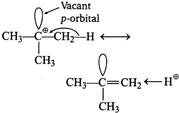 |
| Tertiary butyl carbocation has one vacant p-orbital, hence, it is stabilised by \[\sigma \text{-}p\] (empty) hyperconjugation. |
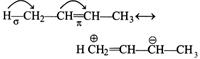 |
| In but-2-ene, stabilisation is due to hyperconjugation between \[\sigma \text{-}{{\pi }^{*}}\]electron delocalisation. |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
