| Consider the following case of completing 1st order reactions. |
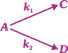 |
| After the start of the reaction at t = 0 with only A, the [C] is equal to the [D] at all times. The time in which all three concentrations will be equal is given by - |
A) \[t=\frac{1}{2{{k}_{1}}}\ell n3\]
B) \[t=\frac{1}{2{{k}_{2}}}\ell n\,3\]
C) \[t=\frac{1}{3{{k}_{1}}}\ell n2\]
D) \[t=\frac{1}{3{{k}_{1}}}\ell n2\]
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
\[{{k}_{1}}={{k}_{2}}\Rightarrow \frac{2}{3}rd\] of A has r exacted for \[\left[ A \right]=\left[ C \right]=\left[ D \right]\] \[\therefore \] \[{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}=\frac{1}{t}\text{ }\ln \text{ }\frac{{{\left[ A \right]}_{0}}}{\frac{1}{3}{{\left[ A \right]}_{0}}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[t=\frac{1}{{{k}_{1}}+{{k}_{2}}}\ln \text{ }3=\frac{1}{2{{k}_{1}}}\ln \text{ }3=\frac{1}{2{{k}_{2}}}\ln \text{ }3\]You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
