A) \[\frac{({{p}^{2}}\text{+}{{q}^{2}})sin\theta }{p\,cos\,\theta +q\,sin\,\theta }\]
B) \[\frac{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}cos}{p\,cos\,\theta +q\,sin\,\theta }\]
C) \[\frac{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}{{{p}^{2}}cos\,\theta +{{q}^{2}}sin\,\theta }\]
D) \[\frac{({{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}})\sin \theta }{{{(pcos\,\theta +qsin\,\theta )}^{2}}}\]
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
\[BD=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}\]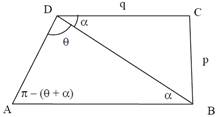 \[\angle ABD=\angle BDC=\alpha \] \[\Rightarrow \]\[\angle DAB=\pi -(\theta +\alpha )\] \[tan\text{ }\alpha =\frac{p}{q}\] \[\Delta ABD\] \[\frac{AB}{\sin \text{ }\theta }=\frac{BD}{\sin (\pi -(\theta +\alpha ))}=\frac{BD}{\sin (\theta +\alpha )}\] \[\therefore \] \[AB=\frac{BD\sin \theta }{\sin (\theta +\alpha )}=\frac{B{{D}^{2}}\sin \theta }{BD\sin (\theta +\alpha )}=\] \[\frac{B{{D}^{2}}\sin \theta }{BD\sin \theta \cos \alpha +BD\cos \theta \sin \alpha }=\frac{({{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}})\sin \theta }{q\sin \theta +p\cos \theta }\]
\[\angle ABD=\angle BDC=\alpha \] \[\Rightarrow \]\[\angle DAB=\pi -(\theta +\alpha )\] \[tan\text{ }\alpha =\frac{p}{q}\] \[\Delta ABD\] \[\frac{AB}{\sin \text{ }\theta }=\frac{BD}{\sin (\pi -(\theta +\alpha ))}=\frac{BD}{\sin (\theta +\alpha )}\] \[\therefore \] \[AB=\frac{BD\sin \theta }{\sin (\theta +\alpha )}=\frac{B{{D}^{2}}\sin \theta }{BD\sin (\theta +\alpha )}=\] \[\frac{B{{D}^{2}}\sin \theta }{BD\sin \theta \cos \alpha +BD\cos \theta \sin \alpha }=\frac{({{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}})\sin \theta }{q\sin \theta +p\cos \theta }\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
