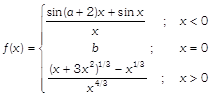 is continuous at \[x=0,\]then \[a+2b\] is equal to [JEE MAIN Held on 09-01-2020 Morning]
is continuous at \[x=0,\]then \[a+2b\] is equal to [JEE MAIN Held on 09-01-2020 Morning]
A) \[-1\]
B) \[1\]
C) \[0\]
D) \[-2\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
[c] \[\underset{x\to {{0}^{-}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{\sin (a+2)x+\sin x}{x}=b=\underset{x\to {{0}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{\left( x+3{{x}^{2}} \right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}}-{{x}^{\frac{1}{3}}}}{{{x}^{\frac{4}{3}}}}\]\[\Rightarrow \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(a+2)+1=b=\underset{x\to {{0}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\frac{{{(1+3x)}^{\frac{1}{3}}}-1}{x}\] \[\Rightarrow \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,a+3=b=\underset{x\to {{0}^{+}}}{\mathop{\lim }}\,\left( \frac{{{(1+3x)}^{\frac{1}{3}}}-1}{(1+3x)-1} \right).3\] \[\Rightarrow \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,a+3=b=\frac{1}{3}.3=1\] \[\Rightarrow \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,a=-2,\,\,b=1\] So, \[a+2b=0\]You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
