| What is 'deficient demand'? Explain the role of 'Bank Rate' in removing it. |
| Or |
| What is 'excess demand'? Explain the role of 'Reverse Repo Rate' in removing it. |
Answer:
Deficit demand refers to a situation where the actual or equilibrium level of demand for output (\[A{{D}_{2}}\]) is less than the full employment level of output (\[A{{D}_{1}}\]). That is,
If \[A{{D}_{2}}\]<\[A{{D}_{1}}\] (situation of Deficit Demand)
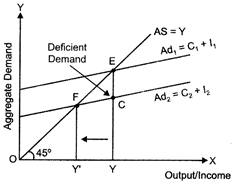
In the figure, \[A{{D}_{1}}\] and AS represents the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve. The economy is at full employment equilibrium at point ?E?, where \[A{{D}_{1}}\] intersects AS curve. At this equilibrium point, or represents the full employment level of output and EY is the aggregate demand at the full employment level of output.
Let us suppose that, the actual aggregate demand for output is only CY, which is lower than EY. This implies that actual aggregate output demanded by the economy CY falls short of the potential (full employment) aggregate output EY. Thus the economy is facing a deficiency in demand. This Bank rare refers to the rate at which the central bank provides loans to the commercial banks. In case or deficit demand, central bank reduces die bank rare. Which reduces the cost of borrowings tor the commercial banks. This implies that people can get loans at cheap rates from the commercial banks. This increases the demand for loans and credits in the market. Therefore, the consumption expenditure increases and finally the aggregate demand increases.
Or
Excess demand refers to a situation where the actual aggregate demand for output \[(A{{D}_{2}})\] is above the full employment level of output \[(A{{D}_{1}}),\] then there exists excess demand. That is,
If \[A{{D}_{2}}\]>\[A{{D}_{1}}\] (situation of Excess Demand)
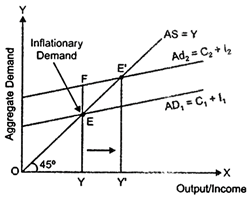
In the figure, \[A{{D}_{1}}\] and AS represents the aggregate demand curve and aggregate supply curve respectively. The economy is at full employment equilibrium at point ?E?, where \[A{{D}_{1}}\] intersects AS curve. At this equilibrium point, OY represents full employment level and EY is aggregate demand at the full employment level of output.
Let us suppose that, the actual aggregate demand for output is FY, which is higher than EY. This implies that actual aggregate output demanded by the economy FY is more than the potential (full employment) aggregate output EY. Thus, the economy is facing surplus demand. This situation is termed as excess demand.
Reverse repo rate refers to the rate at which the Central Bank borrows from the commercial banks. In situation of excess demand, the Central Bank would increase the reverse repo rate. An increase in the reverse repo rate reduces the money supply in the economy, thereby aggregate demand falls.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
