| Define fixed cost. Give an example. Explain with reason the behaviour of Average Fixed cost as output is increased. |
| Or |
| Define marginal product. State the behaviour of margin product when only one input is increased and other inputs are held constant. |
Answer:
Fixed cost: Fixed cost is the cost which does not change with the change in the level of output. This is incurred on fixed factors like machines, building. Fixed cost does not change with the change in the level of output. For eg. a sugar mill usually remains closed for about 3 months in a year for want of raw material but still the mill owner has to incur certain cost like rent of the building, interest on past borrowings, salaries of permanent employees, taxes, etc. On the other hand AFC is fixed cost per unit of output AFC = TFC/Output produced For eg. No of units produced TFC AFC 0 150 \[\infty \] 1 150 150 2 150 75 3 150 50 4 150 37.5 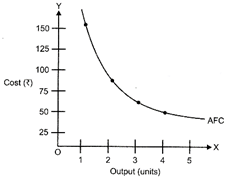
The shape of AFC curve is downward sloping curve from left to right because average fixed cost goes on falling with every increase in the output because TFC remains constant. AFC curve neither touches X?axis because AFC always remain Positive nor touches Y?axis because AFC approach infinity when production is zero. Or Marginal product: Marginal product is an addition to the total product when an additional unit of only variable factor is used, keeping other things same. Marginal product measures extra output per extra unit of input holding all other inputs fixed. Land (fixed Factor) Labour (variable factor) TP AP MP 1 0 0 ? ? 1 1 2 2 2 1 2 6 3 4 1 3 12 4 6 1 4 20 5 8 1 5 25 5 5 1 6 29 4.8 4 1 7 31 4.4 2 1 8 31 3.9 0 1 9 29 3.2 \[2\] 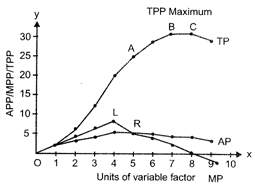
TP increases continuously from point 0 to B. It increases at an increasing rate from 0 to A and at diminishing rate from A to B. TP is maximum at point B and remains up to point C. MP (MPP) curve initially rises, reaches its maximum and ultimately declines taking the shape of inverted\[U\]. AP (APP) curve first rises, reaches its maximum and then declines taking the shape of an inverted\[U\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
