| Distinguish between perfect oligopoly and Imperfect oligopoly. Also explain the "interdependence between the firms" feature of oligopoly. |
| Or |
| Explain the meaning of excess demand and excess supply with the help of a schedule. Explain their effect on equilibrium price. |
Answer:
Difference between perfect oligopoly and imperfect oligopoly: In an oligopoly market when firms produce homogenous products, it is called perfect oligopoly. When firms produce differentiated products it is called imperfect oligopoly. Interdependence between the firms: There is interdependence of firms for taking decision about price and output. Since there are a few firms, a change in price and output of a product by any firm is likely to influence the output and profit of rival firms whose reaction may prove counter-productive. This makes the firms mutually dependent on each other in case of decision about price and output. For example, there is interdependence of decision about price between Pepsi and cola. If Pepsi reduces price, cola-cola may do the same substantially. Or When there is excess demand: Excess demand refers to situation where at a given price, quantity demanded exceed quantity supplied. The situation of excess demand can be explained with the help of following graph and schedule: 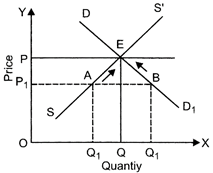
In the above figure, OP is the equilibrium price and \[O{{P}_{1}}\] is the market price. At \[O{{P}_{1}}\] price quantity demanded is OQ and quantity supplied is\[{{Q}_{2}}\]. Thus there is excess demand equal to AB = (\[O{{Q}_{1\,\,}}-\,\,O{{Q}_{2}}\]). This will result in competition among buyers. Price will rise leading to rise in supply and fall in demand as shown by arrows along \[D{{D}_{1}}\]and \[S{{S}_{1}}\] curves. This change will continue till price rises to OP which is the equilibrium price. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied 14 12 10 1 2 3 \[\left. \begin{align} & 7 \\ & 6 \\ & 5 \\ \end{align} \right\}Excess\,\,Supply\] 8 4 4 = Market Equilibrium 6 4 2 5 6 7 \[\left. \begin{align} & 3 \\ & 2 \\ & 1 \\ \end{align} \right\}Excess\,\,Demand\] When there is excess supply: Excess supply refers to a situation where quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded. The situation of excess supply can be explained with help of following graph: 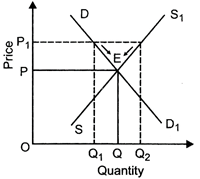
In the above figure, OP is the equilibrium price and \[O{{P}_{1}}\]is the market price. At \[O{{P}_{1}}\] price, quantity supplied is \[O{{Q}_{2}}\]and quantity demanded is\[O{{Q}_{1}}\]. Thus there is excess supply equal to AB = (\[O{{Q}_{1}}\,\,-\,\,O{{Q}_{2}}\]). This will lead to competition among sellers. Price will fall leading to fall in supply and rise in demand as shown by arrows along \[D{{D}_{1}}\] and \[S{{S}_{1}}\] curves. Process of this change will continue till price falls to OP which is equilibrium price.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
