| Show how would you join three resistors, each of resistance \[\mathbf{9}\,\mathbf{\Omega }\] so that the equivalent resistance of the combination is (a) \[\mathbf{13}\mathbf{.5}\,\mathbf{\Omega }\] (b) \[\mathbf{6}\,\mathbf{\Omega }\]? |
| OR |
| (a) Write Joule's law of heating. |
| (b) Two lamps, one rated 100 W; 220 V, and the other 60 W; 220 V, are connected in parallel to electric mains supply. Find the current drawn by two bulbs from the line, if the supply voltage is 220 V. |
Answer:
(a) To get an equivalent resistance of \[13.5\,\Omega ,\] the resistances should be connected as shown in the figure given below:
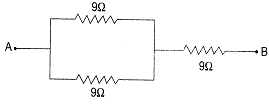
So, \[\frac{1}{{{R}_{P}}}=\frac{1}{{{R}_{1}}}+\frac{1}{{{R}_{2}}}\]
\[=\frac{1}{9}+\frac{1}{9}\]
\[=\frac{1+1}{9}=\frac{2}{9}\]
\[\frac{1}{{{R}_{P}}}=\frac{2}{9}\]
\[{{R}_{P}}=\frac{9}{2}=4.5\Omega \]
Now, \[{{R}_{S}}={{R}_{3}}+4.5\Omega \]
\[=9\,\Omega +4.5\,\Omega \]
\[=13.5\,\Omega \]
(b) To get an equivalent resistance of \[6\,\Omega ,\] the resistances should be connected as shown in the figure given below:
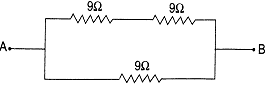
\[{{R}_{S}}={{R}_{1~}}+\,~{{R}_{2}}\]
\[=9+9\]
\[=18\,\Omega \]
Now both the resistors are in parallel with each other so,
\[{{R}_{P}}=\frac{1}{18}+\frac{1}{9}\]
\[=\frac{1+2}{18}=\frac{3}{18}\]
\[=\frac{1}{6}\Omega \]
So, \[{{R}_{P}}=6\,\Omega \]
OR
(a) According to Joule's law of heating, the heat produced in a wire is directly proportional to
(i) square of current \[({{I}^{2}}),\]
(ii) resistance of wire (R),
(iii) time (t) for which current is passed.
Thus, the heat produced in the wire by current in time 't' is
\[H\,\propto \,{{I}^{2}}Rt\]
or \[H=K\,{{I}^{2}}Rt\]
But \[K=1,\] \[H={{I}^{2}}Rt\]
(b) We know that, P = VI
\[\Rightarrow \] \[I=\frac{P}{V}\]
First lamp: \[{{P}_{1}}=100\text{ }W,\text{ }V=220\text{ }volt\]
\[{{I}_{1}}=\frac{{{P}_{1}}}{V}=\frac{100}{220}=0.45A\]
Second lamp: \[{{P}_{2}}=60\text{ }W,\text{ }V=220\text{ }volt\]
\[{{I}_{2}}=\frac{{{P}_{2}}}{V}=\frac{60}{220}=0.27A\]
So, Total current \[={{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}\]
= 0.45 + 0.27
= 0.72 A
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
