LEARINNG OBJECTIVES
This lesson will help you to:—
- learn about the transport of food.
- study about the various plants and animal foods.
- study about community eating.
- study about how food is eaten in mouth, chewed and swallowed.
- learn and study about how animals and birds eat their food.
Real Life Examples
- In Amritsar, langar is offered to the general public throughout the day.
- Now, in India, mid-day meals are being provided in the government school as an incentive to promote education among poor.
QUICK CONCEPT REVIEW
Transport of Food
Food items like cereals, pulses, fruits and vegetables are sown by farmers in fields. The farmer sows seeds of different plants in the field. They require sunlight, water, soil and minerals to grow. The farmers grow them in large fields and take care of them until they grow and are ready to cut.
Later, the farmers sell these food items into the market to sellers. The food items are carried to large distances from the place where they are grown.
The sellers further bring them to us and we buy them.

There are a lot of people involved in this cycle of transfer of food from farmers to us.
The farmers sell the crops to the large mandi. They further transport the crops to very far distances with the help of trucks. The trucks further carry them to the smaller mandis in different cities. The vegetable sellers, fruit sellers and other small cereal sellers buy them from these mandis and sell them to us.
PLANTS AND ANIMAL FOODS
We get food items from both plants arid animals. Food items like fruits, vegetables, cereals and pulses are obtained from plants. Others like milk and milk products (curd, paneer, butter, cheese etc.), meat, eggs. fish, honey are obtained from animals.
Food items can be grouped into the following; Fruits: Mango, Apple, Banana, Cheeku, Grapes, Litchi, Cherry
Vegetables: Potato, Tomato, Cauliflower, Carrot, Peas, Beans
Cereals: Wheat, Rice, Maize, Bajra, Jowar Pulses: Arhar dal, Moong dal. Chickpea (chana), Rajma
Spices: Salt, Pepper, Turmeric and many more Oil seeds: Mustard, flax, corn, wheat etc.
Other food items can be milk and milk products, meat, eggs, fish, honey.
Different vegetables, fruits, cereals and pulses grow in different seasons according to conditions required for them to grow.
Spices: Spice is a dried seed. fruit, root, bark, or vegetative substance primarily used for flavouring, colouring or preserving food. Sometimes a spice is used to hide other flavours. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are parts of leafy green plants also used for flavouring or as garnish.

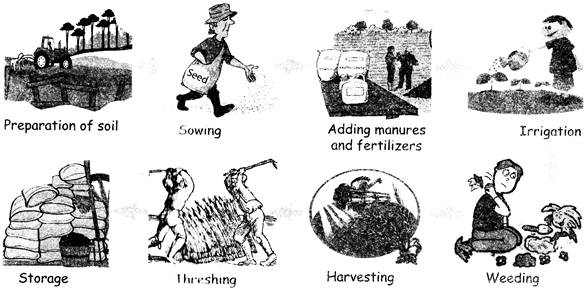
STEPS IN GROWING A CROP
All food items contain five major nutrients
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats
- Vitamins
- Minerals
|
Nutrient
|
Sources
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Patato, banana, sugar, cereals
|
|
Facts
|
Ghee, oil, butter, nuts
|
|
Proteins
|
Pulses, meat, fish, chicken, milk
|
|
Vitamins
|
Green leafy vegetables, fruits, milk
|
|
Minerals
|
Salt, sea food milk egg, spinach
|
Amazing Facts
- Salt which is commonly used as a spice is neither a plant nor animal product. Indeed it is obtained from sea water.
- Honey is the only food that does not spoil
- About 70% of the human body is made of water.
- Sharks lose teeth each week. They get new teeth when they lose the old ones. They may have over 20,000 teeth in a lifetime.
COMMUNITY EATING
- Community eating is the coming together of many people to have a meal. This can be seen on special occasions or festivals.
- The food is cooked in large utensils and in huge quantities to feed many people.
- Community eating' includes langars and mid-day meals in some schools, hostels and boarding.
- The mid-day meal provided in the schools is simple, healthy and wholesome food.
- The food that is made on festivals and occasions also vary considerably from culture to culture.
- In India, huge feasts are arranged on auspicious occasions such as marriages etc.
TONGUE AND TEETH
- As soon as food enters the mouth, it comes in contact with the tongue. Our tongue tastes the food, following which our brain interprets whether the food is sweet, salty, sour or spicy.
- Our teeth help in chewing the food. There are 32 teeth in our mouth.
- Teeth tear the food and break it into smaller pieces so that it can be easily digested.
- The tongue and teeth work in coordination to start the process of digestion in the mouth which gives us the energy we need to live.
- The tongue also plays a vital role in the speech. The way our tongue rolls when we speak determines our speech.
- The tongue is so vital an instrument of speech, it has become an alternate term for language. When people refer to their native or 'mother tongue" they, are referring in part to the tongues close connection to speech.
Historical preview
- Communities in the Fertile crescent region. The name comes from the word “Ceres” the Roman goddess of the harvest.
- Spices were among the most demanded and expensive products available in Europe in the middle ages, the most common being black pepper, cinnamon, cumin, nutmeg, ginger and cloves.
MILK TEETH TO ADULT TEETH
- Babies teeth start to show when they are six or seven months old.
- Most children will have a full set of 20 milk teeth by the time they are three years old.
- At the age of five or six, these teeth are pushed out by permanent teeth growing behind the milk teeth.
- By the age of 14, most children have lost all their milk teeth and have a full set of 28 permanent teeth.
- About around age 20, four more wisdom teeth usually grow in at the back of the mouth.
- They complete the adult set of 32 teeth.
TEETH, BEAKS AND CLAWS
- Like you, some animals have several different kinds of teeth. Others have only one kind. Others don't have any teeth at all. Different types of food require different teeth because food must be broken down into smaller pieces so that it can be digested. Animal's teeth give you clues about what they eat.
- Based on the food they eat, animals can be classified as:
- Herbivorous: Those animals that only eat plants are called herbivorous.
Example: Cow. They have flat teeth.
- Carnivorous: These are flesh eating animals.
Example: Tiger. They usually have sharp teeth.
- Omnivorous: These are those animals that eat both plants as well as animals.
Example: Humans, Baboons, crows etc. They have sharp teeth in front and flat teeth at the back.
- Insectivorous: These are the insect eating animals.
Example: Chameleons.
- Elephants have four sets of teeth in their lifetime. Their tusks are the longest teeth in the world.
Misconcept/Concept
Misconcept: Birds have teeth in their beaks.
Concept: Birds do not have teeth.
Misconcept: The tusk of elephant is actually its horns.
Concept: The tusks are the teeth of the elephant that does not participate in the eating process. Their tusks in made up of ivory that is considered very expensive and because of this, many elephants are being killed.
BACKS AND CLAWS

- Beaks and claws of a bird help in the assembling of food.
- Birds catching their prey with their beaks or claws eat it by their beaks.
- Birds have no teeth. They use their beaks to eat.
- Different birds have different kinds of beaks.
- Some birds use their beaks to protect themselves.
STRONG AND HOOKED BEAKS
- A parrot has a strong and hooked beak. This helps it to easily open nuts and bite hard fruits.
SHORT, HARD AND POINTED BEAK
- Sparrows, finches, pigeons and peacocks have short, hard and pointed beak.
- They eat grains, seeds and crack nuts with the help of their beak.
BOAD AND FLAT BEAK
- A duck has a broad, flat and spoon like beak.
- It can easily dig soft mud near pond to find worms with the help of its beak.
SHARD, STRONG AND POINTED BEAK
- A woodpecker has a sharp, chisel-like beak.
- It makes a hole in the trunk of the tree with the help of its beak and also catches insects.
STRONG, SHARD AND HOOKED BEAKS
- Birds like eagles, vultures and owls have strong, sharp and hooked beaks.
- With the help of their beaks, they can tear up the flesh of their prey easily.
Claws: The feet and claws help the bird in searching food.
- Hens scratch the ground with their claws to eat insects and seeds.
- Birds like eagles, vultures and owls have strong and sharp claws to help them catch their prey. These claws are called talons.




