Answer:
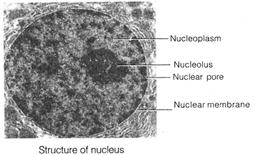
(i) Nucleus It is a double membrane bounded protoplasmic body that carries hereditary information. Chemically it contains DNA, basic proteins, non-basic proteins, RNA, lipids and minerals, etc.
Nucleus has main parts, nucleoplasm, chromatin and nucleolus.
(a) Nuclear envelope It is made up of two nuclear membranes separated by 10-70 nm perinuclear space. The outer membrane is rough due to the presence of ribosomes. Nuclear envelope has many pores with diameter 200-800 ![]() .
(b) Nucleoplasm or nuclear matrix It is a colloidal complex that fills the nucleus. Nucleoplasm contains raw material for synthesis of DNA and RNA.
(c) Chromatin It is a fibrous hereditary material formed by DNA-histone complex. Some non-histone proteins and also RNA. A single human cell has about 2 metre long thread of DNA distributed among its 46 chromosomes.
(d) Nucleolus It was originally discovered by Fontana (1781) and given the present name by Bowman (1840). It is naked roughly rounded darkly stained structure that is attached to chromatin at specific spot called Nucleolar Organiser Region (NOR). Nucleolus is the site for elaboration of rRNA and synthesis of ribosomes. It is therefore, known as ribosomal factory.
.
(b) Nucleoplasm or nuclear matrix It is a colloidal complex that fills the nucleus. Nucleoplasm contains raw material for synthesis of DNA and RNA.
(c) Chromatin It is a fibrous hereditary material formed by DNA-histone complex. Some non-histone proteins and also RNA. A single human cell has about 2 metre long thread of DNA distributed among its 46 chromosomes.
(d) Nucleolus It was originally discovered by Fontana (1781) and given the present name by Bowman (1840). It is naked roughly rounded darkly stained structure that is attached to chromatin at specific spot called Nucleolar Organiser Region (NOR). Nucleolus is the site for elaboration of rRNA and synthesis of ribosomes. It is therefore, known as ribosomal factory.
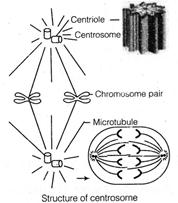
 (ii) Centrosome It is an organelle usually containing two cylindrical structure called centrioles. They are surrounded by amorphous pericentriolar materials. Both the centrioles in a centrosome lie perpendicular to each other in which each has an orgnisation like the cartwheel. They are made up of nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin protein the central past of the proximal region of centriole is called hub, which is connected with tubules of the peripheral triplet by radial spokes made of protein. The centriole form the basal bodies of cilia or flagella and spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division in animal life.
(ii) Centrosome It is an organelle usually containing two cylindrical structure called centrioles. They are surrounded by amorphous pericentriolar materials. Both the centrioles in a centrosome lie perpendicular to each other in which each has an orgnisation like the cartwheel. They are made up of nine evenly spaced peripheral fibrils of tubulin protein the central past of the proximal region of centriole is called hub, which is connected with tubules of the peripheral triplet by radial spokes made of protein. The centriole form the basal bodies of cilia or flagella and spindle fibres that give rise to spindle apparatus during cell division in animal life.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
