Answer:
Long Answer Type Questions
All organisms are made
up of cells, which further organises themselves into tissues,organs and organ
systems. Thus, forming the building blocks of organisms cells also theproperty
of totipotency, capable of developing into a new organism.
Besides, forming the
structural unit they perform different specialised functions in the sameway as
each organ or system carries out in an organism. Thus, exhibiting division of
labour i.e., cell organelles are specific in their functions.
Structure
Function
Diagram
1. Cell membrane all cell
possess a phospholipid based cell membrane.
The cell membrane is
selectively permeable, i.e., only selected material can pass through it.
2. Cytoplasm It is a watery
solution containing controlled concentration of organic and inorganic
compounds.
It functions as a site for
metabolism and provide energy and material for growth and reproduction.
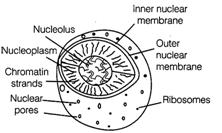
3. Nucleus It essentially
consists of DNA, the nuclear matrix or the nucleoplasm containing nucleolus
and chromatin.
It serves to store and
transmit information to direct the synthetic activities of the entire cell.
In also transfers the genetic
information required for growth and reproduction.
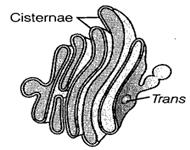
4. Golgi apparatus (Golgi
complex) They constitute of many flat disc shaped sacs or cistermae of
![]() diameter.
These stacks are arranged parallel to each other.
diameter.
These stacks are arranged parallel to each other.
These are mainly involved in
packaging the materials to be delivered either to intracellular targets or
secreted outside the cells.
All these factors, i.e,,
structural an a functional attributes it to
De cane a a living ceil.
Structure
Function
Diagram
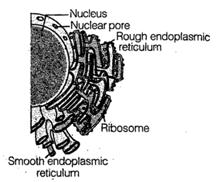
5. The F-endoplasmic
Reticulum (ER, ER is often an extensive 3- dimensional network of intra
cellular membranes formed by three elements- cisternae, tubules and vesicles
The ER bearing ribosomes on
it surface is called rough endoplasmic reticulum (CRER). These are involved
in protein synthesis and secretion. The ER without Fibosomes are called smooth
endoplasmic reticulum involved in synthesis of lipids like steroidal
hormones.
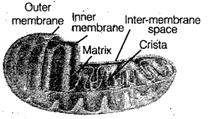
6. Mitochondria Mitochondria
is a double membrane bound structure with outer and inner membrane dividing
its lumen into two compartments, i.e., outer membrane forming of organelle
and inner membrane forming number of infoldings called the cristae.
Mitochondria are-the sites
for aerobic respiration. It is known as power house of 'the cell since
producing cellular energy in the form; ofATP.
7. Lysosomes These
aremembrane bound vesicular structures, formed -by the process of packaging
in the Golgi apparatus.
These are rich in many types
of hydrolytic enzymes (hydrolases- lipases, proteases, carbohydrates).
8. Vacuoles The vacuole is-
the membrane bound-.space found in the cytoplasm, it .contain water, sap,
excretory product and other material not useful for the cell. The vacuole is
bound by single membrane called tonoplast.
In. plants the tonoplast facilitates
the transport of a number, of ions and other materials against concentration
gradients" into the vacuole.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
