Answer:
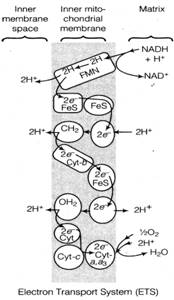
Electron Transport System (ETS) The metabolic pathway through which the electron passes from one carrier to another, is called the Electron Transport System (ETS).
(i) It occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
(ii) Electrons from NADH produced in the mitochondrial matrix during citric acid cycle are oxidised by an NADH dehydrogenase (complex-I).
(iii) They are then transferred to ubiquinone located within the inner membrane.
(iv) Ubiquinone also receives reducing equivalents via FADH2 (complex-III) that is generated during oxidation of succinate in the citric acid cycle.
(v) The reduced ubiquinone (ubiquinol) is then oxidised with the transfer of electrons to cytochrome-c via cytochrome-toci complex (complex-Ill).
(vi) Cytochrome-c is a small protein attached to the outer surface of the inner membrane.
(vii) When the electrons pass from one carrier to another via complex-I to Iv in the electron transport chain, they are coupled to ATP synthase (complex-v) for the production of ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate.
(viii) The number of ATP molecules synthesised depends on the nature of the electron donor.
(ix) Oxidation of one molecule of NADH gives rise to 3 molecules of ATP, while that of one molecule of FADH2produces 2 molecules of ATP.
(x) Although, the aerobic process of respiration takes place only in the presence of oxygen, the role of oxygen is limited to the terminal stage of the process. Yet, the presence of oxygen is vital, since, it drives the whole process by removing hydrogen from the system.
(xi) Oxygen acts as the final hydrogen acceptor.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
