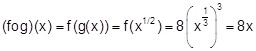 E4.
If
E4.
If 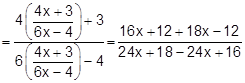
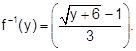 Sol.
Given f(x) = 9x2 + 6x ? 5, Df = R+
Injectivity
: Let x1, x2 be any two elements of R+
such that f(x1) = f(x2)
Sol.
Given f(x) = 9x2 + 6x ? 5, Df = R+
Injectivity
: Let x1, x2 be any two elements of R+
such that f(x1) = f(x2)
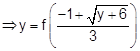
Answer:
Let
g1 and g2 are two inverses of f
Therefore
for al ![]() (fog1)
(y) = f(g1(y)) = y
(fog1)
(y) = f(g1(y)) = y
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is
invertible function
is
invertible function ![]() is
one-one]
is
one-one]
![]()
![]() inverse of f
is unique.
inverse of f
is unique.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
