Answer:
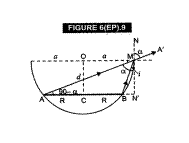
m Fig. 6(EP).9, we have
shown an opaque hemispherical howl of radius a with centre 0.
A circular
disc of radius R with centre C is placed co-axially and horizontally inside the
bowl. We have to calculate OC = d.
AMA'
is the direction of incident ray before liquid is filled in the bowl. When
liquid of refractive index p. is filled in the bowl, the near edge B of the
disc just becomes visible. Here, BM is the incident ray, which is refracted
along MA'. N/N? is normal to the horizontal surface of liquid in the bowl. i is
the angle of incidence and r = ![]() is the angle of
refraction.
As
refraction occurs at M in going from denser to rarer medium, therefore,
according to Snell's law
is the angle of
refraction.
As
refraction occurs at M in going from denser to rarer medium, therefore,
according to Snell's law
![]() ?(i
?(i
 Now,
Now,
![]() and
and![]() Putting
in (i),we get
Putting
in (i),we get
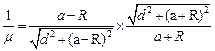 or
or
![]() On simplifying, we get
On simplifying, we get
![]()
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
