Triangles and Their Properties
Category :
Triangles and Their Properties
TRIANGLE
A figure bounded by three line segments in a plane is called a triangle. It has three vertices, three sides and three angles.
Types of a Triangle
Triangle further divided into following types
Acute Angled Triangle When all three angles of triangle
are acute, then it is an acute angled triangle.
Right Angled Triangle When one triangle of triangle is
\[90{}^\circ ,\] then it is called right angled triangle.
Obtuse Angled Triangle When one angle of the triangle
is obtuse angle, then triangle is called obtuse
angled triangle,
Scalene Triangle When all three sides of triangle are of
different length, then triangle is scalene triangle.
Isosceles Triangle When two sides of triangle are of
equal length, then triangle is called isosceles. Two angles of isosceles triangle are also equal.
Equilateral Triangle It has all three sides of equal length.
It has all three angles as \[60{}^\circ .\]
Properties of Triangle
(i) Sum of three angles of a triangle are always \[180{}^\circ .\]
(ii) Sum of length of any two sides of triangle is greater than the length of third sides and different of any two sides of a triangle is less than third side.
(iii) Sides opposite to the greatest angle is the longest side.
(iv) Sides opposite to equal angles are equal.
(v) The exterior angles of a triangle (at each vertex) is equal to the sum of the two opposite interior angles.
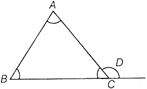
\[\angle D=\angle A+\angle B\]
Area of a Triangle
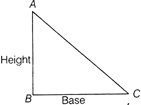
Right Angled Triangle Let \[\Delta \] indicates the area
\[\Delta =\frac{1}{2}\times \text{Base}\times \text{Height}\]
any Triangl \[\Delta =\sqrt{s\,(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}\]
[where, \[s,=\frac{a+b+c}{2}\] it is called semi perimeter
and sides are a, b, c]
Equilateral Triangle
\[\Delta =\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}{{(side)}^{2}}\]
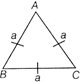
Circle Inscribed in a triangle
\[\begin{matrix}
\Delta =r\times s & \left[ \begin{matrix}
\text{where}\,r=\text{inradius}, \\
s=\text{semiperimeter} \\
=\frac{a+b+c}{2} \\
\end{matrix} \right] \\
\end{matrix}\]
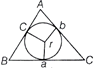
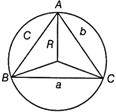
Triangle is inscribed in a circle
\[\begin{matrix}
\Delta =\frac{abc}{4R} & \left[ \begin{matrix}
\text{where}\,a,\,\,b\,\text{and}\,c\,\text{are}\,\text{the} \\
\text{side}\,\text{and}\,R\,\text{circumradius} \\
\end{matrix} \right] \\
\end{matrix}\]
CONGRUENT TRIANGLES
Two triangles are said to be congruent, if all sides, angles of one triangle are equal to corresponding sides and angles of another triangle.
Condition for congruency have been given below
SSS It means side-side-side, if all three sides of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then the two triangles are congruent.
SAS It means side-angle-side, if two sides and included angle of one triangle are equal to the corresponding sides and included angle of another triangle, then triangle are congruent.
ASA It means angle-side-angle, if two angle and included side of one triangle are equal to two angles and included side of another triangle, then triangles are congruent.
RHS It means right-hypotenuse-side if hypotenuse and one side of a right triangle is equal to hypotenuse and one side of another right triangle, then triangles are congruent.
Medians
The line segment joining a vertex of triangle to mid-point of opposite side- is called medians.
Medians of triangle pass through common points,
· Which divides each median in 2 : 1.
· If two medians of a triangle are equal, then triangle is isosceles.
ALTITUDE
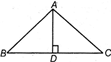
A line segment from a vertex which is perpendicular to opposite side of triangle is called altitude. Here, in the given triangle, AD is an altitude,
SIMILAR TRIANGLES
Two triangles are said to be similar, if they are alike in shapes only. The corresponding angles of two similar triangles are equal but the corresponding sides are only proportional and not equal.
Condition for similarity of Two Triangles
· The three angles of one triangle are respectively to the three angles of the second triangle.
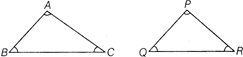
· Two sides of one triangle are proportional two sides of the other and included angles are equal
(i) Ratio of sides = Ratio of heights = Ratio of medians
= Ratio of angular bisectors
(ii) Ratio of area = Ratio of square of corresponding sides.
Result of Similar Triangles
Theorem 1 If line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle intersecting the other two sides, then it divides these sides in the same ratio
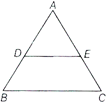
Here, \[DE\parallel BC,\]
\[\frac{AD}{BD}=\frac{AE}{EC}\] or \[\frac{AD}{AB}=\frac{AE}{AC}\]
or \[\frac{AB}{DB}=\frac{AC}{EC}\]
Theorem 2 The ratio of areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of any two corresponding sides
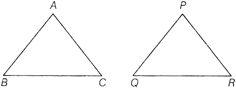
Here, \[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta PQR\]
Then, \[\frac{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta ABC}{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta PQR}=\frac{A{{B}^{2}}}{P{{Q}^{2}}}=\frac{B{{C}^{2}}}{Q{{R}^{2}}}=\frac{A{{C}^{2}}}{P{{R}^{2}}}\]
Theorem 3 The areas of two similar triangles are in the ratio of the squares of corresponding altitudes,
Here, \[\Delta ABC\tilde{\ }\Delta PQR\]
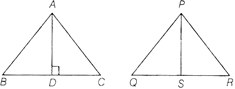
Then, \[\frac{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta ABC}{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta PQR}=\frac{A{{D}^{2}}}{P{{S}^{2}}}\]
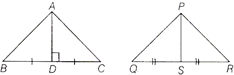
Theorem 4 The areas of two similar triangle are in the ratio of the squares of the corresponding medians.
Here,\[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta PQR\]
Then,\[\frac{Area\,ofABC}{Area\,of\,\Delta PQR}=\frac{A{{D}^{2}}}{P{{S}^{2}}}\]
Theorem 5 The areas of two similar triangles are in the ratio of square of the corresponding angle bisector segments.
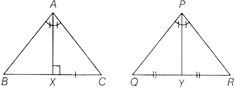
Here, \[\Delta ABC\sim \Delta PQR\]
Then, \[\frac{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta ABC}{\text{Area}\,\text{of}\,\Delta PQR}=\frac{A{{X}^{2}}}{A{{Y}^{2}}}\]
Theorem 6 If the area of two similar triangles are equal, then the triangles are congruent.
or Equal and similar triangles are congruent.
Theorem 7 (mid-point theorem) The line joining the mid-points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side and is half of the third side.
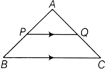
Here, P and Q are mid-point of AB and AC.
So \[PQ=\frac{1}{2}BC\]
Circumcentre
The point of intersection of perpendicular bisector of sides in a triangle is called the circumcentre.
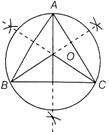
Here, 0 in \[\Delta ABC\]is the point of intersection of also
AO = OC = OB = circum radii
In this portion
· acute triangle is inside the triangle.
· obtuse triangle is outside the triangle.
· right triangle is the mid-point of the hypotenuse.
INCENTRE
The point of intersection of the angle bisector of a triangle is called the incentre.
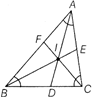
e.g. In the triangle shown AD, BE and CF are the angle bisector of LA, LB and LC, respectively and their point of intersection which is I is the incentre of \[\Delta \,ABC.\]
ORTHOCENTRE
The point of intersection of perpendicular or altitude in a triangle is called the orthocentre. e.g. in\[\Delta ABC\], shown 0 is the point of intersection of three altitudes AD, BE and
CF
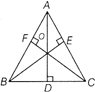
e.g., In\[\Delta ABC\]shown 0 is the point of intersection of three altitudes AD, BE and CF
\[\angle BOC=180{}^\circ -\angle \,A\]
\[\angle AOC=180{}^\circ -\angle B\]
\[\angle AOB=180{}^\circ -\angle C\]
The position of orthocenter in a
· acute triangle is inside the triangle
· obtuse triangle is outside the triangle
· right triangle is the right angle vertex.
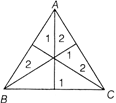
CENTROID
The point of intersection of medians in a triangle is called the centroid.
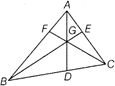
e.g. In\[\Delta ABC\] shown G is the centroid, is the point of intersection of medians AD, BE and CF
Centroid devides the medians in 2:1 ratio.
i.e. AG : GD = BG : GE = CG : GF = 2 : 1
The centroid divides the triangle into 6 triangles of equal area.
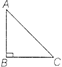
Pythagoras Theorem
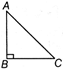
In a right angled triangle, right angle at B,
\[A{{B}^{2}}+B{{C}^{2}}=A{{C}^{2}}\]
Apollonius Theorem
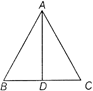
In \[\Delta ABC,\] if \[AD\]is the median,
Then, \[A{{B}^{2}}+A{{C}^{2}}=2(A{{D}^{2}}+B{{D}^{2}})\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
