A) \[\mathbf{i}+2\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k}\]
B) \[\mathbf{i}-2\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{k}\]
C) \[-\mathbf{i}-2\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k}\]
D) \[\mathbf{i}+2\mathbf{j}-\mathbf{k}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
Let Q be the image of the point \[P(\mathbf{i}+3\mathbf{k})\] in the plane \[\mathbf{r}.(\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k})=1\]. Then PQ is normal to the plane. Since PQ passes through P and in normal to the given plane, therefore equation of PQ is \[\mathbf{r}=(\mathbf{i}+3\mathbf{k})+\lambda (\mathbf{i}+\mathbf{j}+\mathbf{k})\]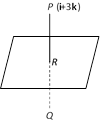 |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
