| Directions : (11-15) |
| Temperature Dependence of Resistivity |
| The resistance of a conductor at temperature \[t{}^\circ C\] is given by \[{{R}_{t}}={{R}_{0}}\left( 1+\alpha t \right)\] |
| Where \[{{R}_{t}}\] is the resistance at \[t{}^\circ C\], \[{{R}_{0}}\] is the resistance at \[0{}^\circ C\] and \[\alpha \] is the characteristics constants of the material of the conductor. |
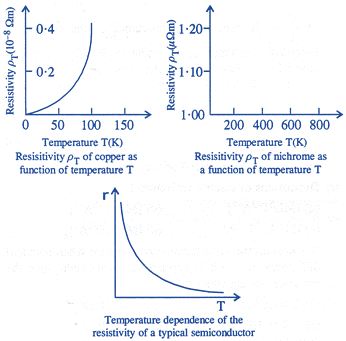
| Over a limited of range of temperatures, that is not too large. The resistivity of a metallic conductor is approximately given by \[{{\rho }_{t}}={{\rho }_{0}}\left( 1+\alpha t \right)\]. |
| Where \[\alpha \] is the temperature coefficient of resistivity. Its unit is \[{{K}^{-1}}\]or \[{}^\circ {{C}^{-1}}\]. |
| For metals \[\alpha \] is positive i.e., resistance increases with rise in temperature. |
| For insulators and semiconductors, \[\alpha \] is negative i.e., resistance decreases with rise in temperature. |
 |
A) resistivity
B) temperature coefficient of resistivity
C) conductivity
D) drift velocity
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
Temperature coefficient of resistivity is defined as the fractional increase in resistivity per unit increase in temperature.You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
