| Directions : (46 - 50) |
| Parallel Sheet of Charge |
| Surface charge density is defined as charge per unit surface area of surface charge distribution i.e., |
| \[\sigma =\frac{dq}{dS}\]. Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs having magnitude of \[17\centerdot 0\times {{10}^{-22}}\,C\,\,{{m}^{-2}}\] as shown. The intensity of electric field at a point is\[E=\frac{\sigma }{{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}\], where \[{{\varepsilon }_{0}}\]= permittivity of free space. |
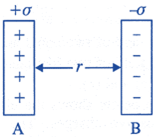 |
A) \[17\times {{10}^{-22}}N/C\]
B) \[1\centerdot 5\times {{10}^{-25}}\,N/C\]
C) \[1\centerdot 9\times {{10}^{-10}}\,N/C\]
D) zero
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
There are two plates A and B having surface charge densities,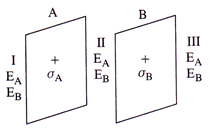 \[{{\sigma }_{A}}=17\,.\,0\times {{10}^{-22}}C/{{m}^{2}}\] on A and \[{{\sigma }_{B}}=-17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}\,C/{{m}^{2}}\] on B, respectively, According to Gauss's theorem, if the plates have same surface charge density but having opposite sings, then the electric field in region I is zero. \[{{E}_{1}}={{E}_{A}}+{{E}_{B}}=\frac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}+\left( -\frac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right)=0\]
\[{{\sigma }_{A}}=17\,.\,0\times {{10}^{-22}}C/{{m}^{2}}\] on A and \[{{\sigma }_{B}}=-17.0\times {{10}^{-22}}\,C/{{m}^{2}}\] on B, respectively, According to Gauss's theorem, if the plates have same surface charge density but having opposite sings, then the electric field in region I is zero. \[{{E}_{1}}={{E}_{A}}+{{E}_{B}}=\frac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}}+\left( -\frac{\sigma }{2{{\varepsilon }_{0}}} \right)=0\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
