A) \[90{}^\circ \]
B) \[120{}^\circ \]
C) \[150{}^\circ \]
D) \[160{}^\circ \]
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
Let PX, QY, RZ be the altitudes from P, Q, R which meet the opposite sides at X, Y, Z respectively go that their point of intersection O is the orthocentre.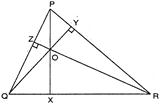 From right angled As PQ X and PRX \[P{{Q}^{2}}=Q{{X}^{2}}+P{{X}^{2}}\] and \[P{{R}^{2}}=P{{X}^{2}}+X{{R}^{2}}\] \[\therefore \] \[PQ=PR\] Similarly \[QR=PR\] Thus \[PQ=PR=QR\] so that \[\Delta PQR\] is an equilateral \[\therefore \] \[\angle P={{60}^{o}}\] Hence, \[\angle QOR=2\angle P\] (given) \[=2\times {{60}^{o}}={{120}^{o}}\]
From right angled As PQ X and PRX \[P{{Q}^{2}}=Q{{X}^{2}}+P{{X}^{2}}\] and \[P{{R}^{2}}=P{{X}^{2}}+X{{R}^{2}}\] \[\therefore \] \[PQ=PR\] Similarly \[QR=PR\] Thus \[PQ=PR=QR\] so that \[\Delta PQR\] is an equilateral \[\therefore \] \[\angle P={{60}^{o}}\] Hence, \[\angle QOR=2\angle P\] (given) \[=2\times {{60}^{o}}={{120}^{o}}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
