Answer:
Suppose body is freely falling from point A, where its initial velocity \[{{u}_{1}}=0.\] Let B be the point where its final velocity becomes \[{{V}_{1}}=v.\] Before coming to point B, it will cover a distance of \[{{S}_{1}}=h\] Acceleration of the body \[{{a}_{1}}=+g\] Let C be the point where its velocity \[({{v}^{2}})\]becomes 2v. Distance covered \[({{S}_{2}})\] before reaching point \[{{R}_{1}}=R\] 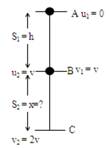
\[{{v}^{2}}=2gh\] ?..(1) \[3{{v}^{2}}=2gx\] ?.(2) Substituting (1) in (2), we get, \[3\,2gh=2gx\] \[x=3h\] AB BC \[{{u}_{1}}=0\] \[{{u}_{2}}=v\] \[{{v}_{1}}=v\] \[{{v}_{2}}=2v\] \[{{S}_{1}}=h\] \[{{S}_{2}}=x=?\] \[{{a}_{1}}=+g\] \[{{a}_{2}}=+g\] \[({{v}^{2}})-({{0}^{2}})=2gh\] \[{{(2v)}^{2}}-{{v}^{2}}=2gx\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
