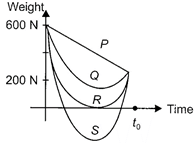
A) P
B) Q
C) R
D) S
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
Weight of passenger on Earth \[\text{= m}\times {{\text{g}}_{e}}\text{= 60}\times \text{10= 600 N}\] Weight of passenger on Mars \[=m\times {{g}_{m}}=60\times 4=240N\] As the passenger is going from the Earth to the Mars in a spaceship moving with a constant velocity so the acceleration due to gravity because of Earth and Mars becomes negligible (zero) at some point in space. Thus, weight of passenger becomes zero. After some time, as he reaches near to the Mars, his weight increases because of acceleration due to gravity of Mars. Finally, at the surface of Mars, his weight becomes 240 N.You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
