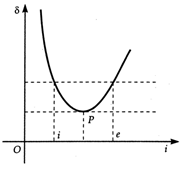
 Explain why any given value of \['\delta '\] corresponds to two values of angle of incidence. State the significance of point 'P' on the graph. Use this information to derive an expression for refractive index of the material of the prism.
Explain why any given value of \['\delta '\] corresponds to two values of angle of incidence. State the significance of point 'P' on the graph. Use this information to derive an expression for refractive index of the material of the prism.
Answer:
In general, any given value of \[\delta \] (except for \[i=e\]) corresponds to two values \[i\] and e. This, in fact, is expected from the symmetry of \[\text{i}\] and e as \[\delta =i+e-\] A i.e., \[\delta \] remains the same if \[i\] and e are interchanged. 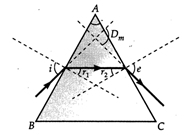 Point P is the point of minimum deviation. This is related to the fact that the path of the ray, as shown in. Fig. can be traced back, resulting in the same angle of deviation. At the minimum deviation \[{{D}_{m}},\]the refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to the base. For \[\delta ={{D}_{m}},\] \[i=e\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{r}_{1}}={{r}_{2}}\] \[\therefore \] \[2r=A\] or \[r=\frac{A}{2}\] Similarly, \[{{D}_{m}}=2i-A\]or \[i=\frac{A+{{D}_{m}}}{2}\] \[\therefore \] The refractive index of the prism is \[\mu =\frac{\sin (A+{{D}_{m}})/2}{\sin A/2}\]
Point P is the point of minimum deviation. This is related to the fact that the path of the ray, as shown in. Fig. can be traced back, resulting in the same angle of deviation. At the minimum deviation \[{{D}_{m}},\]the refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to the base. For \[\delta ={{D}_{m}},\] \[i=e\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{r}_{1}}={{r}_{2}}\] \[\therefore \] \[2r=A\] or \[r=\frac{A}{2}\] Similarly, \[{{D}_{m}}=2i-A\]or \[i=\frac{A+{{D}_{m}}}{2}\] \[\therefore \] The refractive index of the prism is \[\mu =\frac{\sin (A+{{D}_{m}})/2}{\sin A/2}\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
