A) \[t\,\left( 1-\frac{1}{\mu } \right)\] away
B) \[t\,\left( 1+\frac{1}{\mu } \right)\] away
C) \[t\,\left( 1-\frac{1}{\mu } \right)\] nearer
D) \[t\,\left( 1+\frac{1}{\mu } \right)\] nearer
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
Normal shift \[\Delta x=\left( 1-\frac{1}{\mu } \right)\ t\]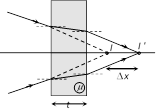 and shift takes place in direction of ray.
and shift takes place in direction of ray.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
