A) \[\sqrt{2}\]
B) \[2\sqrt{2}\]
C) \[3\sqrt{2}\]
D) None of these
Correct Answer: B
Solution :
| [b] The area bounded by the curve |
| \[y=1+\frac{8}{{{x}^{2}}},\] x-axis and the ordinates \[x=2,x=4\]is |
| \[=\int_{2}^{4}{ydx}\] |
| \[=\int_{2}^{4}{\left( 1+\frac{8}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)dx}\] |
| \[=\left[ x-\frac{8}{x} \right]_{2}^{4}=4\]. |
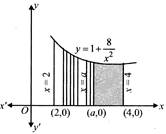 |
| Since, \[x=a\] divides this area into two equal parts, |
| \[\therefore \] Required area \[=2\int_{2}^{a}{y\,\,dx}\] |
| \[\therefore \,\,\,\,\,\,\,4=2\int_{2}^{a}{\left( 1+\frac{8}{{{x}^{2}}} \right)dx}\] |
| \[\Rightarrow 2=\left[ x-\frac{8}{x} \right]_{2}^{a}=\left( a-\frac{8}{a} \right)-(2-4)\] |
| \[\Rightarrow {{a}^{2}}=8\therefore a=2\sqrt{2}\] |
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
