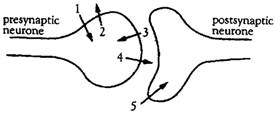
 What are the substances moving across the membranes?
What are the substances moving across the membranes?
A)
1
2
3
4
5
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
Ach.
\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
B)
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]
Ach.
C)
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]
Ach.
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
D)
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
\[{{K}^{+}}\]
\[N{{a}^{+}}\]
Ach.
\[C{{a}^{2+}}\]
Correct Answer: C
Solution :
[c] As the action potential reaches the synapse, the pre-synaptic membrane is depolarised due to the entry of sodium ions (1). The membrane is subsequently repolarised by the exit of potassium ions (2). The arrival of the action potential cause calcium channels in the membrane to open, thus calcium ions rush into the synaptic knob (3). This causes the synaptic vesicles to fuse with the pre-synaptic membrane, releasing acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft (4). Acetylcholine binds to specific receptor sites on the post- synaptic membrane, opening ion channels and causing sodium ions to enter (5), depolarising the membrane.You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
