A) \[(x-3y)(x+3y)=0\]
B) \[(x-3y)(x+y)=0\]
C) \[(3x-y)(3x+y)=0\]
D) None of these
Correct Answer: A
Solution :
The three given points are \[O\,\,(0,\,\,0),\,\,A(0,\,\,4)\] and \[B\,(6,\,\,0)\] and let \[P(x,\,\,y)\] be the moving point. Area of \[\Delta POA=2\,.\,\]Area of \[\Delta POB\]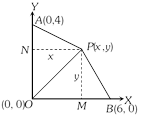 \[\Rightarrow \,\,\frac{1}{2}\times 4\times x=\pm \,2\times \frac{1}{2}\times 6\times y\] or \[x=\pm \,3y\] Hence the equation to both parts of the locus of P is \[(x-3y)\,(x+3y)=0\].
\[\Rightarrow \,\,\frac{1}{2}\times 4\times x=\pm \,2\times \frac{1}{2}\times 6\times y\] or \[x=\pm \,3y\] Hence the equation to both parts of the locus of P is \[(x-3y)\,(x+3y)=0\].
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
