| (i) What are linked genes? |
| (ii) TH Morgan selected fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster) for his experiment inspite of its small size. Give reasons. |
| (iii) How are linkage and crossing over opposite to each other? |
| Or |
| A particular garden pea plant produces only violet flowers. |
| (i) Is it homozygous dominant for the trait or heterozygous? |
| (ii) How would you determine its genotype? Explain with the help of crosses. |
| (iii) In a test cross, when double heterozygous is crossed with double recessive, what ratio is obtained in \[{{F}_{1}}\]-generation? |
Answer:
(i) Linked genes are present on the same chromosome and are placed together very closely in a linear sequence. These genes do not show independent assortment and produce only parental type of progeny. They give a dihybrid ratio of 3 : 1 and test cross ratio of 1 : 1. (ii) Morgan worked with the fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) which were found to be suitable for genetic studies due to the following characteristics (a) They could be grown on simple synthetic medium in the laboratory. (b) They complete their life cycle in about two weeks. (c) A single mating could produce a large number of progeny flies. (d) A clear differentiation of the sexes, i.e. the male and female are easily distinguishable. (e) It has many types of variation (hereditary) that can be seen with low power microscopes. (ii) Linkage is the tendency of certain loci or alleles (genes) to be inherited together while, crossing over is the segregation of genes. The genes on a chromosome either follow linkage path or cross over, to form the gametes during gametogenesis. Or (i) It must be homozygous dominant since, it produces only violet flowers. It means that two copies of same dominant allele is carried by the organism (V V-Violet). (ii) To ensure the genotype, the plant must be crossed with a plant bearing white (recessive) flowers (test cross). (a) If the progeny obtained consists of violet flowers, plant is homozygous dominant. (b) If the progeny contains both violet and white flowered plants, the plant is heterozygous. Cross I Homozygous dominant 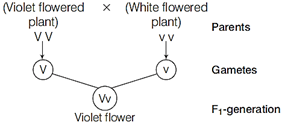
Cross II Heterzygous 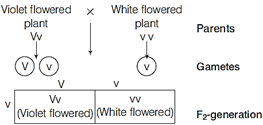
(iii) In case, a double heterozygous is crossed with double recessive, in \[{{F}_{1}}\]-generation 1 : 1 : 1 : 1 ratio is obtained.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
