| We see advertisements like 'Saheli' as a method of family planning. |
| (i) What is 'Saheli'? |
| (ii) What is the principle behind using it as a method to control population growth? |
| (iii) How will you convenience people who say it is religiously wrong to use them to avoid pregnancy? |
| (iv) Mention the advantages of it. |
| OR |
| (i) Give the name of the structures, parts A and B shown in the diagram below develop into. |
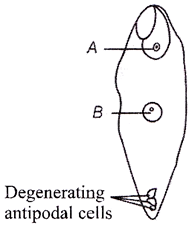 |
| (ii) Explain the process of development which B undergoes in albuminous and exalbuminous seeds. Give one example of each of these seeds. |
Answer:
(i) 'Saheli' is an oral contraceptive pill, which inhibits ovulation and fertilisation.
(ii) The basic principle of using this is to control population growth. It is the easiest way of inhibiting ovulation and implantation.
Pills have to be taken per 21 days starting within the first five days of menstrual cycle. These pills inhibits the motility and secretory activity of oviducts.
(iii) Although, it is said that it is religiously wrong to use pills to avoid pregnancy as people believe that giving a birth to a child is a God's gift and we should never abort it. But the people are unaware that population is increasing day-by-day due to which, resources are diminishing and becoming unavailable to the existing population. So, in my opinion it is a myth that using pills to avoid pregnancy is religiously wrong.
(iv) Advantages of using pills are as follows
(a) It has a very low failure rate as these are easy and convenient to use.
(b) It regulates menstrual bleeding and reduces the chances of anaemia.
(c) It reduces premenstrual symptoms and pain associated with menstruation.
(d) It reduces the risk of ovarian and uterine cancer as well as ovarian cysts and pelvic inflammatory disease in women.
OR
(i) Part A develops into the embryo. The part B develops into the endosperm.
(ii) Part B undergoes endospore formation.
The process is as follows:
(a) Primary endosperm cell divides repeatedly and forms triploid endosperm tissue.
(b) Primary endosperm tissue undergoes successive free nuclear divisions to give rise to free nuclei. At this stage, it is called free nuclear endosperm.
(c) Wall formation takes place from the periphery and proceeds towards the centre and the endosperm becomes cellular.
(d) In albuminous seeds, some amount of endosperm persists in the mature seeds and be used up during seed germination, e.g., wheat and maize.
(e) In exalbuminous seeds, the endosperm is completely consumed by the developing embryo before seed maturation e.g., pea, groundnut.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
