Answer:
Equilibrium price is determined by the forces of market demand and market supply. Considering market demand schedule on the one hand and market supply schedule on the other hand, we identify equilibrium price as the one where market demand is equal to market supply i.e. where market demand curve and market supply curve intersect each other. 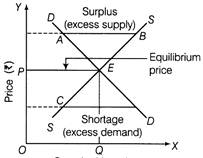 Quantity (dozen) Determination of Equilibrium Price The equilibrium price will remain the same even when demand and supply curves shift rightwards when the percentage increase in quantity demanded is same as the percentage increase in quantity supplied. From the figure, it is clear that the rightward shift in demand curve from DD to\[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\], is proportionately equal to the rightward shift in supply curve from SS to\[{{S}_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\]. The new equilibrium point is\[{{E}_{1}}\]. Equilibrium price remains the same at OP, but equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to.\[O{{Q}_{1}}\]
Quantity (dozen) Determination of Equilibrium Price The equilibrium price will remain the same even when demand and supply curves shift rightwards when the percentage increase in quantity demanded is same as the percentage increase in quantity supplied. From the figure, it is clear that the rightward shift in demand curve from DD to\[{{D}_{1}}{{D}_{1}}\], is proportionately equal to the rightward shift in supply curve from SS to\[{{S}_{1}}{{S}_{1}}\]. The new equilibrium point is\[{{E}_{1}}\]. Equilibrium price remains the same at OP, but equilibrium quantity rises from OQ to.\[O{{Q}_{1}}\] 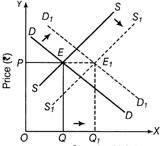 Quantity (Units) Diagram showing Increase in Equilibrium Output when Increase in Demand is Equal to Increase in Supply.
Quantity (Units) Diagram showing Increase in Equilibrium Output when Increase in Demand is Equal to Increase in Supply.
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
