A) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\,\tan \theta ={{a}^{2}}\]
B) \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}+2xy\,\tan \theta ={{a}^{2}}\]
C) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+2xy\,\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}\]
D) \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}+2xy\,\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}\]
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
Given \[\angle A-\angle B=\theta \Rightarrow \tan (A-B)=\tan \theta \] \[\Rightarrow \,\frac{\tan A-\tan B}{1+\tan A-\tan B}=\tan \theta \] ?.(i) In right angled triangle CDA, \[\tan A=\frac{k}{a-h}\]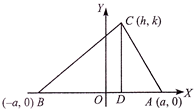 Similarly in triangle CDB, \[\tan B=\frac{k}{a+h}\] Substitute the values of tan A and tan B in (i), we get \[{{h}^{2}}-{{k}^{2}}+2hk\,\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}\] Hence the locus is \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}.\]
Similarly in triangle CDB, \[\tan B=\frac{k}{a+h}\] Substitute the values of tan A and tan B in (i), we get \[{{h}^{2}}-{{k}^{2}}+2hk\,\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}\] Hence the locus is \[{{x}^{2}}-{{y}^{2}}+2xy\cot \theta ={{a}^{2}}.\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
