A) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{k}^{2}}\]
B) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=2{{k}^{2}}\]
C) \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=3{{k}^{2}}\]
D) None of these
Correct Answer: D
Solution :
Let the coordinates of A and B be (.a, 0) and (0, &) respectively. Clearly, AOAB is a right angled triangle, the hypotenuse AB is a diameter of the circle.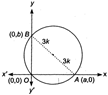 \[\therefore \]\[AB=2(3k)=6k\] \[\therefore \]Now, OA2+OB2=AB2 \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=36{{k}^{2}}\] ...(i) Let \[(\alpha ,\beta )\] be the coordinates of the centroid of \[\Delta OAB,\] thence \[\alpha =\frac{a}{3},\beta =\frac{b}{3}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[a=3\alpha \]and \[b=3\beta .\] From Eq. (i), \[{{(3\alpha )}^{2}}+{{(3\beta )}^{2}}=36{{k}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{\alpha }^{2}}+{{\beta }^{2}}=4{{k}^{2}}\] Thus, the locus of centroid of \[\Delta OAB\] is\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4{{k}^{2}}.\]
\[\therefore \]\[AB=2(3k)=6k\] \[\therefore \]Now, OA2+OB2=AB2 \[\Rightarrow \]\[{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}=36{{k}^{2}}\] ...(i) Let \[(\alpha ,\beta )\] be the coordinates of the centroid of \[\Delta OAB,\] thence \[\alpha =\frac{a}{3},\beta =\frac{b}{3}\] \[\Rightarrow \]\[a=3\alpha \]and \[b=3\beta .\] From Eq. (i), \[{{(3\alpha )}^{2}}+{{(3\beta )}^{2}}=36{{k}^{2}}\] \[\Rightarrow \] \[{{\alpha }^{2}}+{{\beta }^{2}}=4{{k}^{2}}\] Thus, the locus of centroid of \[\Delta OAB\] is\[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=4{{k}^{2}}.\]
You need to login to perform this action.
You will be redirected in
3 sec
